| Issue |
A&A
Volume 600, April 2017
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A65 | |
| Number of page(s) | 10 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201630008 | |
| Published online | 31 March 2017 | |
Radiative age mapping of the remnant radio galaxy B2 0924+30: the LOFAR perspective⋆
1 ASTRON, The Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy, Postbus 2, 7990 AA Dwingeloo, The Netherlands
e-mail: shulevski@astron.nl
2 University of Groningen, Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, Landleven 12, 9747 AD Groningen, The Netherlands
3 Obserwatorium Astronomiczne, Uniwersytet Jagielloński, ul Orla 171, 30-244 Kraków, Poland
4 IRA-INAF, via P. Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
5 Leiden Observatory, Leiden University, Niels Bohrweg 2, 2333 CA Leiden, The Netherlands
6 INAF–Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari, via della Scienza 5, 09047 Selargius (CA), Italy
7 Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Open University, Walton Hall, Milton Keynes MK7 6AA, UK
8 RAL Space, The Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Space Science and Technology Department, Chilton, Didcot, Oxfordshire OX11 0QX, UK
9 School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK
10 University of Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany
Received: 3 November 2016
Accepted: 5 January 2017
We have observed the steep spectrum radio source B2 0924+30 using the LOw Frequency ARray (LOFAR) telescope. Hosted by a z = 0.026 elliptical galaxy, it has a relatively large angular size of 12′ (corresponding to 360 kpc projected linear size) and a morphology reminiscent of a remnant Fanaroff-Riley type II (FRII) radio galaxy. Studying active galactic nuclei (AGN) radio remnants can give us insight into the time-scales involved into the episodic gas accretion by AGNs and their dependence on the AGN host environment. The proximity of the radio galaxy allows us to make detailed studies of its radio structure and map its spectral index and radiative age distribution. We combine LOFAR and archival images to study the spectral properties at a spatial resolution of 1′. We derive low frequency spectral index maps and use synchrotron ageing models to infer ages for different regions of the source. Thus, we are able to extend the spectral ageing studies into a hitherto unexplored frequency band, adding more robustness to our results. Our detailed spectral index mapping, while agreeing with earlier lower resolution studies, shows flattening of the spectral index towards the outer edges of the lobes. The spectral index of the lobes is 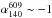 and gradually steepens to
and gradually steepens to 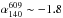 moving towards the inner edges of the lobes. Using radiative ageing model fitting we show that the AGN activity ceased around 50 Myr ago. We note that the outer regions of the lobes are younger than the inner regions which is interpreted as a sign that those regions are remnant hotspots. We demonstrate the usefulness of maps of AGN radio remnants taken at low frequencies and suggest caution over the interpretation of spectral ages derived from integrated flux density measurements versus age mapping. The spectral index properties as well as the derived ages of B2 0924+30 are consistent with it being an FRII AGN radio remnant. LOFAR data are proving to be instrumental in extending our studies to the lowest radio frequencies and enabling analysis of the oldest source regions.
moving towards the inner edges of the lobes. Using radiative ageing model fitting we show that the AGN activity ceased around 50 Myr ago. We note that the outer regions of the lobes are younger than the inner regions which is interpreted as a sign that those regions are remnant hotspots. We demonstrate the usefulness of maps of AGN radio remnants taken at low frequencies and suggest caution over the interpretation of spectral ages derived from integrated flux density measurements versus age mapping. The spectral index properties as well as the derived ages of B2 0924+30 are consistent with it being an FRII AGN radio remnant. LOFAR data are proving to be instrumental in extending our studies to the lowest radio frequencies and enabling analysis of the oldest source regions.
Key words: galaxies: active / radio continuum: galaxies / galaxies: individual: B2 0924+30
The LOFAR and WSRT images used to derive the spectral index and ageing maps are available at the CDS via anonymous ftp to cdsarc.u-strasbg.fr (130.79.128.5) or via http://cdsarc.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/qcat?J/A+A/600/A65
© ESO, 2017
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


