| Issue |
A&A
Volume 578, June 2015
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A47 | |
| Number of page(s) | 15 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201525817 | |
| Published online | 02 June 2015 | |
Obscuration in active galactic nuclei: near-infrared luminosity relations and dust colors
1 Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1312, Gießenbachstr., 85741 Garching, Germany
e-mail: burtscher@mpe.mpg.de
2 Raymond and Beverly Sackler School of Physics & Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, 69978 Ramat Aviv, Israel
Received: 5 February 2015
Accepted: 5 April 2015
We combine two approaches to isolate the AGN luminosity at near-IR wavelengths and relate the near-IR pure AGN luminosity to other tracers of the AGN. Using integral-field spectroscopic data of an archival sample of 51 local AGNs, we estimate the fraction of non-stellar light by comparing the nuclear equivalent width of the stellar 2.3 μm CO absorption feature with the intrinsic value for each galaxy. We compare this fraction to that derived from a spectral decomposition of the integrated light in the central arcsecond and find them to be consistent with each other. Using our estimates of the near-IR AGN light, we find a strong correlation with presumably isotropic AGN tracers. We show that a significant offset exists between type 1 and type 2 sources in the sense that type 1 sources are 7 (10) times brighter in the near-IR at 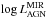 = 42.5 (
= 42.5 (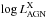 = 42.5). These offsets only become clear when treating infrared type 1 sources as type 1 AGNs. All AGNs have very red near- to mid-IR dust colors. This, as well as the range of observed near-IR temperatures, can be explained with a simple model with only two free parameters: the obscuration to the hot dust and the ratio between the warm and hot dust areas. We find obscurations of
= 42.5). These offsets only become clear when treating infrared type 1 sources as type 1 AGNs. All AGNs have very red near- to mid-IR dust colors. This, as well as the range of observed near-IR temperatures, can be explained with a simple model with only two free parameters: the obscuration to the hot dust and the ratio between the warm and hot dust areas. We find obscurations of 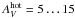 mag for infrared type 1 sources and
mag for infrared type 1 sources and 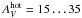 mag for type 2 sources. The ratio of hot dust to warm dust areas of about 1000 is nicely consistent with the ratio of radii of the respective regions as found by infrared interferometry.
mag for type 2 sources. The ratio of hot dust to warm dust areas of about 1000 is nicely consistent with the ratio of radii of the respective regions as found by infrared interferometry.
Key words: radiation mechanisms: thermal / techniques: high angular resolution / techniques: imaging spectroscopy / galaxies: active / galaxies: nuclei / galaxies: Seyfert
© ESO, 2015
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


