| Issue |
A&A
Volume 545, September 2012
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A28 | |
| Number of page(s) | 9 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201219896 | |
| Published online | 31 August 2012 | |
Constraints on cosmic-ray efficiency in the supernova remnant RCW 86 using multi-wavelength observations
1
Université Bordeaux 1, CNRS/IN2P3,
Centre d’Études Nucléaires de Bordeaux
Gradignan,
33175
Gradignan,
France
e-mail: lemoine@cenbg.in2p3.fr
2
Funded by contract ERC-StG-259391 from the European Community
France
3
Laboratoire Univers et Particules de Montpellier, Université
Montpellier 2, CNRS/IN2P3, 34095
Montpellier Cedex 5,
France
e-mail: mrenaud@lupm.univ-montp2.fr
4
Astronomical Institute, Utrecht University,
PO Box 80000,
3508 TA
Utrecht, The
Netherlands
5
MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research,
Cambridge,
MA
02139,
USA
6
Department of Physics and Mathematics, Aoyama Gakuin University
5-10-1 Fuchinobe, Chuo-ku,
Sagamihara, 252-5258
Kanagawa,
Japan
7
Dipartimento di Fisica “M. Merlin” dell’Universitá e del
Politecnico di Bari, 70126
Bari,
Italy
8
Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Sezione di Bari,
70126
Bari,
Italy
9
W. W. Hansen Experimental Physics Laboratory, Kavli Institute for
Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Department of Physics and SLAC National
Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, Stanford, CA
94305,
USA
Received:
26
June
2012
Accepted:
19
July
2012
Context. Several young supernova remnants (SNRs) have recently been detected in the high-energy (HE; 0.1 < E < 100 GeV) and very-high-energy (VHE; E > 100 GeV) gamma-ray domains. As exemplified by RX J1713.7−3946, the nature of this emission has been hotly debated, and direct evidence for the efficient acceleration of cosmic-ray protons at the SNR shocks still remains elusive.
Aims. We study the broadband gamma-ray emission from one of these young SNRs, namely RCW 86, for which several observational lines of evidence indirectly point towards the presence of accelerated hadrons. We then attempt to detect any putative hadronic signal from this SNR in the available gamma-ray data, in order to assess the level of acceleration efficiency.
Methods. We analyzed more than 40 months of data acquired by the Large Area Telescope (LAT) on-board the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope in the HE domain, and gathered all of the relevant multi-wavelength (from radio to VHE gamma-rays) information about the broadband nonthermal emission from RCW 86. For this purpose, we re-analyzed the archival X-ray data from the ASCA/Gas Imaging Spectrometer (GIS), the XMM-Newton/EPIC-MOS, and the RXTE/Proportional Counter Array (PCA).
Results. Beyond the expected Galactic diffuse background, no significant
gamma-ray emission in the direction of RCW 86 is detected in any of the 0.1–1, 1–10
and 10–100 GeV Fermi-LAT maps. The derived HE upper limits, together with
the H.E.S.S. measurements in the VHE domain, are incompatible with a standard
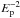 hadronic emission arising from proton-proton interactions, and can only be accommodated by
a spectral index Γ ≤ 1.8, i.e. a value in-between the standard (test-particle) index and
the asymptotic limit of theoretical particle spectra in the case of strongly modified
shocks. In such a hadronic scenario, the total energy in accelerated particles is at the
level of
hadronic emission arising from proton-proton interactions, and can only be accommodated by
a spectral index Γ ≤ 1.8, i.e. a value in-between the standard (test-particle) index and
the asymptotic limit of theoretical particle spectra in the case of strongly modified
shocks. In such a hadronic scenario, the total energy in accelerated particles is at the
level of 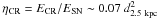 /
/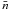 (with the distance
d2.5 kpc ≡ d/2.5 kpc
and the effective density
(with the distance
d2.5 kpc ≡ d/2.5 kpc
and the effective density 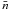 ≡
≡
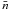 /1 cm-3),
and the average magnetic field must be stronger than 50 μG in order to
significantly suppress any leptonic contribution. On the other hand, the interpretation of
the gamma-ray emission by inverse Compton scattering of high energy electrons reproduces
the multi-wavelength data using a reasonable value for the average magnetic field
of 15–25 μG. In this leptonic scenario, we derive a conservative upper
limit to ηCR of 0.04 d
/1 cm-3),
and the average magnetic field must be stronger than 50 μG in order to
significantly suppress any leptonic contribution. On the other hand, the interpretation of
the gamma-ray emission by inverse Compton scattering of high energy electrons reproduces
the multi-wavelength data using a reasonable value for the average magnetic field
of 15–25 μG. In this leptonic scenario, we derive a conservative upper
limit to ηCR of 0.04 d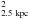 /
/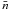 .
We discuss these results in the light of existing estimates of the magnetic field
strength, the effective density and the acceleration efficiency in RCW 86.
.
We discuss these results in the light of existing estimates of the magnetic field
strength, the effective density and the acceleration efficiency in RCW 86.
Key words: ISM: individual objects: RCW 86 / ISM: individual objects: G315.4 / 2.3 / ISM: individual objects: MSH 14 / 63 / gamma rays: general / ISM: supernova remnants
© ESO, 2012
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


