| Issue |
A&A
Volume 539, March 2012
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A33 | |
| Number of page(s) | 10 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201118254 | |
| Published online | 22 February 2012 | |
Overdensities of 24 μm sources in the vicinities of high-redshift radio galaxies
1 Institute for Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh, EH9 3HJ, UK
e-mail: jhm@roe.ac.uk
2 European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching, Germany
3 INAF – Osservatorio di Roma, via Frascati 33, 00040 Monteporzio Catone, Italy
4 CSIRO Astronomy & Space Science, PO Box 76, Epping, NSW 1710, Australia
5 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91101, USA
Received: 12 October 2011
Accepted: 24 December 2011
We present a statistical study of the environments of 63 high-redshift radio galaxies (HzRGs) between redshifts 1 ≤ z ≤ 5.2, using the 24 μm waveband of the MIPS instrument aboard the Spitzer Space Telescope. Using a counts-in-cell analysis, a statistically significant source overdensity is found in 1.75′ radius circular cells centred on the HzRGs when compared to reference fields. We report an average overdensity of
δ 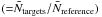 = 2.2 ± 1.2
at a flux density cut of f24 μm = 0.3 mJy. This result implies that HzRGs are likely to lie in protoclusters of active and star-forming galaxies at high redshift. Over 95% of our targeted HzRGs lie in higher than average density fields. Further, 20 (32%) of our selected fields are found to be overdense to at least a 3σ significance, of which 9 are newly identified protocluster candidates. We observe a weak correlation between redshift and 24 μm source density, and discuss the populations being probed at different redshifts. In our uniformly selected sample, which was designed to cover two orders of magnitude in radio luminosity throughout z = 1−4, we find that the 24 μm source density does not depend on radio luminosity. We also compare this result with recent work describing IRAC source overdensities around the same HzRGs and find correlations between the results.
= 2.2 ± 1.2
at a flux density cut of f24 μm = 0.3 mJy. This result implies that HzRGs are likely to lie in protoclusters of active and star-forming galaxies at high redshift. Over 95% of our targeted HzRGs lie in higher than average density fields. Further, 20 (32%) of our selected fields are found to be overdense to at least a 3σ significance, of which 9 are newly identified protocluster candidates. We observe a weak correlation between redshift and 24 μm source density, and discuss the populations being probed at different redshifts. In our uniformly selected sample, which was designed to cover two orders of magnitude in radio luminosity throughout z = 1−4, we find that the 24 μm source density does not depend on radio luminosity. We also compare this result with recent work describing IRAC source overdensities around the same HzRGs and find correlations between the results.
Key words: large-scale structure of Universe / infrared: galaxies / galaxies: clusters: general / galaxies: evolution / galaxies: formation
© ESO, 2012
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


