| Issue |
A&A
Volume 518, July-August 2010
Herschel: the first science highlights
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | L138 | |
| Number of page(s) | 5 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014585 | |
| Published online | 16 July 2010 | |
Letter to the Editor
A Herschel PACS and SPIRE study of the dust content of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant *,**
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK e-mail: mjb@star.ucl.ac.uk
2
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117
Heidelberg, Germany
3
Space Science and Technology Department, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Oxfordshire, OX11 0QX, UK
4
UK Astronomy Technology Centre, Royal Observatory Edinburgh, Blackford Hill, Edinburgh EH9 3HJ, UK
5
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Nottingham, University Park,
Nottingham NG7 2RD, UK
6
School of Physics and Astronomy, Cardiff University, The Parade, Cardiff,
Wales CF24 3AA, UK
7
Dept of Astronomy, Stockholm University, AlbaNova University Center,
Roslagstulsbacken 21, 10691 Stockholm, Sweden
8
Institute for Space Imaging Science, University of Lethbridge, Lethbridge,
Alberta, TJ1 1B1, Canada
Received:
30
March
2010
Accepted:
12
May
2010
Using the 3.5-m Herschel Space Observatory, imaging photometry of
Cas A has been obtained in six bands between 70
and 500 μm with the PACS and SPIRE instruments, with angular
resolutions ranging from 6 to 37”.
In the outer regions of the remnant the 70-μm PACS image
resembles the 24-μm image Spitzer image, with the emission
attributed
to the same warm dust component, located in the reverse shock region. At
longer wavelengths, the three SPIRE bands are increasingly dominated by
emission from cold interstellar dust knots and filaments,
particularly across the central, western and southern parts of the
remnant. Nonthermal emission from the northern part of the remnant
becomes prominent at 500 μm. We have estimated and subtracted the
contributions from the nonthermal, warm dust and cold interstellar dust
components. We confirm and resolve for the first time a cool
(~35 K) dust component, emitting at 70-160 μm, that is located
interior to the reverse shock region, with an estimated mass of
0.075 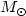 .
.
Key words: ISM: supernova remnants / dust, extinction / Infrared: ISM
Herschel is an ESA space observatory with science instruments provided by European-led Principal Investigator consortia and with important participation from NASA.
Figure 3 is only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


