| Issue |
A&A
Volume 516, June-July 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | A46 | |
| Number of page(s) | 22 | |
| Section | Stellar atmospheres | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913825 | |
| Published online | 24 June 2010 | |
The Hamburg/ESO R-process enhanced star survey (HERES)*,**
V. Detailed abundance analysis of the r-process enhanced star HE 2327-5642
1
Universitäts-Sternwarte München, Scheinerstr. 1, 81679 München,
Germany e-mail: lyuda@usm.lmu.de
2
Institute of Astronomy, Russian Academy of Sciences, 119017 Moscow,
Russia e-mail: lima@inasan.ru
3
Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg, Landessternwarte,
Königstuhl 12, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail: N.Christlieb@lsw.uni-heidelberg.de
4
Department of Astronomy and Space Physics, Uppsala University, Box 515,
75120 Uppsala, Sweden
5
Observatoire de Paris, GEPI and URA 8111 du CNRS, 92195 Meudon Cedex,
France
6
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University, East
Lansing, MI 48824, USA
Received:
8
December
2009
Accepted:
8
March
2010
Aims. We present a detailed abundance analysis of a strongly r-process enhanced giant star discovered in the HERES project, HE 2327–5642, for which [Fe/H] = -2.78, [r/Fe] = +0.99.
Methods. We determined the
stellar parameters and element abundances by analyzing the
high-quality VLT/UVES spectra. The surface gravity was calculated from the
non-local thermodynamic equilibrium (NLTE) ionization balance between
 and
and 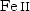 , and
, and 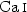 and
and 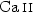 .
.
Results. Accurate abundances for a total of 40 elements and for 23 neutron-capture elements beyond Sr and up to Th were determined in HE 2327–5642. For every chemical species, the dispersion in the single line measurements around the mean does not exceed 0.11 dex. The heavy element abundance pattern of HE 2327–5642 is in excellent agreement with those previously derived for other strongly r-process enhanced stars, such as CS 22892-052, CS 31082-001, and HE 1219-0312. Elements in the range from Ba to Hf match the scaled Solar r-process pattern very well. No firm conclusion can be drawn about the relationship between the fisrt neutron-capture peak elements, Sr to Pd, in HE 2327–5642 and the Solar r-process, due to the uncertainty in the Solar r-process. A clear distinction in Sr/Eu abundance ratios was found between the halo stars of different europium enhancement. The strongly r-process enhanced stars contain a low Sr/Eu abundance ratio at [Sr/Eu] = -0.92 ± 0.13, while the stars with 0 < [Eu/Fe] < 1 and [Eu/Fe] < 0 have 0.36 dex and 0.93 dex higher Sr/Eu values, respectively. Radioactive dating for HE 2327–5642 with the observed thorium and rare-earth element abundance pairs results in an average age of 13.3 Gyr, when based on the high-entropy wind calculations, and 5.9 Gyr, when using the Solar r-residuals. We propose that HE 2327–5642 is a radial-velocity variable based on our high-resolution spectra covering ~4.3 years.
Key words: stars: abundances / stars: atmospheres / stars: fundamental parameters / nuclear reactions, nucleosynthesis, abundances
Based on observations collected at the European Southern Observatory, Paranal, Chile (Proposal numbers 170.D-0010, and 280.D-5011).
Table 8 is only available in electronic form at http://www.aanda.org
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


