| Issue |
A&A
Volume 513, April 2010
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | L11 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014124 | |
| Published online | 29 April 2010 | |
Letter to the Editor
Periodic mass-loss episodes due to an oscillation mode with variable amplitude in the hot supergiant HD 50064*
1
Instituut voor Sterrenkunde, K.U. Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200D, 3001
Leuven, Belgium e-mail: conny.aerts@ster.kuleuven.be
2
Department of Astrophysics, IMAPP, University of Nijmegen, PO Box 9010, 6500 GL Nijmegen, The Netherlands
3
Belgisch Instituut voor Ruimte Aeronomie (BIRA), Ringlaan 3, 1180 Brussels,
Belgium
4
LESIA, CNRS UMR8109, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Université Denis Diderot, Observatoire de Paris, 92195 Meudon Cedex, France
5
Institut d'Astrophysique et de Géophysique, Université de Liège, Allée du 6 Août 17, 4000 Liège, Belgium
6
Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, CNRS/Université Paris XI UMR 8617, 91405 Orsay, France
Received:
25
January
2010
Accepted:
28
March
2010
Aims. We aim to interpret the photometric and spectroscopic variability of the luminous blue variable supergiant HD 50064 (V = 8.21).
Methods. CoRoT space photometry and follow-up high-resolution spectroscopy with a time base of 137 d and 169 d, respectively, was gathered, analysed, and interpreted using standard time series analysis and light curve modelling methods, as well as spectral line diagnostics.
Results. The space photometry reveals one period of 37 d, which undergoes a sudden amplitude change with a factor 1.6. The pulsation
period is confirmed in the spectroscopy, which additionally reveals metal line
radial velocity values differing by ~30 km s-1 depending on the
spectral line and on the epoch. We estimate Teff ~ 13 500 K,
log g ~ 1.5 from the equivalent width of Si lines. The Balmer lines reveal
that the star undergoes episodes of changing mass loss on a time scale similar
to the changes in the photometric and spectroscopic variability, with an average value of log 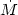
 -5
(in M
-5
(in M yr-1). We
tentatively interpret the 37 d period as the result of a strange
mode oscillation.
yr-1). We
tentatively interpret the 37 d period as the result of a strange
mode oscillation.
Key words: asteroseismology / stars: oscillations / stars: winds, outflows / stars: individual: HD 50064 / stars: atmospheres / supergiants
Based on high-resolution spectroscopy assembled with the CORALIE spectrograph attached to the 1.2 m Euler telescope at La Silla, Chile and on CoRoT space-based photometry. The CoRoT space mission was developed and is operated by the French space agency CNES, with the participation of ESA's RSSD and Science Programmes, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Germany, and Spain.
© ESO, 2010
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


