| Issue |
A&A
Volume 508, Number 3, December IV 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1313 - 1330 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200913327 | |
| Published online | 04 November 2009 | |
REM near-IR and optical photometric monitoring of pre-main sequence stars in Orion *,**,***
Rotation periods and starspot parameters
1
INAF, Osservatorio Astrofisico di Catania, via S. Sofia, 78, 95123 Catania, Italy e-mail: antonio.frasca@oact.inaf.it
2
INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, via Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy
3
European Space Agency (ESTEC), PO Box 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands
4
Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
5
Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg, Sternwarte 5, 07778 Tautenburg, Germany
Received:
21
September
2009
Accepted:
24
October
2009
Aims. We aim at determining the rotational periods and the starspot properties in very young low-mass stars belonging to the Ori OB1c star forming region, contributing to the study of the angular momentum and magnetic activity evolution in these objects.
Methods. We performed an intensive photometric monitoring of the PMS stars falling in a field
of about 10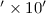 in the vicinity of the Orion nebula cluster (ONC),
also containing the BD eclipsing system 2MASS J05352184-0546085.
Photometric data were collected between November 2006 and January 2007 with the REM telescope
in the
in the vicinity of the Orion nebula cluster (ONC),
also containing the BD eclipsing system 2MASS J05352184-0546085.
Photometric data were collected between November 2006 and January 2007 with the REM telescope
in the 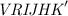 bands.
The largest number of observations is in the I band (about 2700 images)
and in J and H bands (about 500 images in each filter).
From the observed rotational modulation, induced by the presence of surface inhomogeneities,
we derived the rotation periods.
The long time-baseline (nearly three months) allowed us
to detect rotation periods, also for the slowest rotators, with sufficient accuracy (
bands.
The largest number of observations is in the I band (about 2700 images)
and in J and H bands (about 500 images in each filter).
From the observed rotational modulation, induced by the presence of surface inhomogeneities,
we derived the rotation periods.
The long time-baseline (nearly three months) allowed us
to detect rotation periods, also for the slowest rotators, with sufficient accuracy (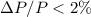 ).
The analysis of the spectral energy distributions and, for some stars, of high-resolution
spectra provided us with the main stellar parameters (luminosity, effective temperature,
mass, age, and
).
The analysis of the spectral energy distributions and, for some stars, of high-resolution
spectra provided us with the main stellar parameters (luminosity, effective temperature,
mass, age, and 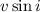 ) which are essential for the discussion of our results.
Moreover, the simultaneous observations in six bands, spanning from optical to
near-infrared wavelengths, enabled us to derive the starspot properties for these very
young low-mass stars.
) which are essential for the discussion of our results.
Moreover, the simultaneous observations in six bands, spanning from optical to
near-infrared wavelengths, enabled us to derive the starspot properties for these very
young low-mass stars.
Results. In total, we were able to determine the rotation periods for 29 stars, spanning from about 0.6 to 20 days. Thanks to the relatively long time-baseline of our photometry, we derived periods for 16 stars and improved previous determinations for the other 13. We also report the serendipitous detection of two strong flares in two of these objects. In most cases, the light-curve amplitudes decrease progressively from the R to H band as expected for cool starspots, while in a few cases, they can only be modelled by the presence of hot spots, presumably ascribable to magnetospheric accretion. The application of our own spot model to the simultaneous light curves in different bands allowed us to deduce the spot parameters and particularly to disentangle the spot temperature and size effects on the observed light curves.
Key words: stars: pre-main sequence / stars: rotation / stars: starspots / stars: flare / techniques: photometric / ISM: individual objects: Orion
Based on observations collected at the ESO REM telescope (La Silla, Chile) and at the MMT Observatory, a joint facility of the Smithsonian Institution and the University of Arizona.
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


