| Issue |
A&A
Volume 507, Number 1, November III 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 195 - 208 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200912626 | |
| Published online | 03 September 2009 | |
Deep U-B-V imaging of the Lockman Hole with the LBT*
Observations and number counts
1
Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstraße, 85748 Garching, Germany e-mail: erovilos@mpe.mpg.de
2
Institute of Physics, Eötvös University, Pázmány P. s. 1/A, 1117 Budapest, Hungary
3
Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik, Boltzmannstraße 2, 85748, Garching, Germany
4
Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, 933 North Cherry Avenue, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
5
California Institute of Technology, MC 205-24, 1200 East California Boulevard, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
Received:
3
June
2009
Accepted:
25
August
2009
We used the large binocular camera (LBC) mounted on the large binocular
telescope (LBT) to observe the Lockman Hole in the U, B, and V bands. Our
observations cover an area of 925 arcmin2. We reached depths of 26.7,
26.3, and 26.3 mag(AB) in the three bands, respectively, in terms of 50%
source detection efficiency, making this survey the deepest U-band survey
and one of the deepest B and V band surveys with respect to its covered area.
We extracted a large number of sources (~89 000), detected
in all three bands
and examined their surface density, comparing it with models of galaxy
evolution. We find good agreement with previous claims of a steep faint-end
slope of the luminosity functions, caused by late-type and irregular
galaxies at 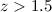 . A population of dwarf star-forming galaxies at
. A population of dwarf star-forming galaxies at
 is needed to explain the U-band number counts. We also find
evidence of strong supernova feedback at high redshift.
This survey is complementary to the r, i, and z Lockman Hole survey conducted
with the Subaru telescope and provides the essential wavelength coverage
to derive photometric redshifts and select different types of sources from
the Lockman Hole for further study.
is needed to explain the U-band number counts. We also find
evidence of strong supernova feedback at high redshift.
This survey is complementary to the r, i, and z Lockman Hole survey conducted
with the Subaru telescope and provides the essential wavelength coverage
to derive photometric redshifts and select different types of sources from
the Lockman Hole for further study.
Key words: surveys / galaxies: photometry
Based on data acquired using the large binocular telescope (LBT). The LBT is an international collaboration among institutions in the United States, Italy, and Germany. LBT Corporation partners are the University of Arizona on behalf of the Arizona university system; Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, Italy; LBT Beteiligungsgesellschaft, Germany, representing the Max-Planck Society, the Astrophysical Institute Potsdam, and Heidelberg University; Ohio State University, and the Research Corporation, on behalf of the University of Notre Dame, the University of Minnesota, and the University of Virginia.
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


