| Issue |
A&A
Volume 506, Number 3, November II 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1199 - 1213 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200912068 | |
| Published online | 18 August 2009 | |
The inner rim structures of protoplanetary discs
1
Anton Pannekoek Astronomical Institute, University of Amsterdam, PO Box 94249, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands e-mail: M.Kama@uva.nl
2
Utrecht Astronomical Institute, University of Utrecht, PO Box 80000, 3508 TA Utrecht, The Netherlands
3
Department of Astrophysics, Radboud University Nijmegen, Postbus 9010, 6500 GL Nijmegen, The Netherlands
Received:
13
March
2009
Accepted:
27
July
2009
The inner boundary of protoplanetary discs is structured by the dramatic opacity changes at the transition from the
dust-containing to a dust-free zone. This paper explores the variety and limits of inner rim structures in passively heated
dusty discs. For this study, we implemented detailed sublimation physics in a fast Monte Carlo radiative transfer code. We show that
the inner rim in dusty discs is not an infinitely sharp wall but a diffuse region which may be narrow or wide. Furthermore, high surface
densities and large silicate grains as well as iron and corundum grains decrease the rim radius, from a 2.2 AU radius for small silicates
around a 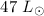 Herbig Ae star typically to 0.4 AU and as close as 0.2 AU. A passive disc with grain growth and a diverse dust
composition must thus have a small inner rim radius. Finally, an analytical expression is presented for the rim location as a function of
dust, disc and stellar properties.
Herbig Ae star typically to 0.4 AU and as close as 0.2 AU. A passive disc with grain growth and a diverse dust
composition must thus have a small inner rim radius. Finally, an analytical expression is presented for the rim location as a function of
dust, disc and stellar properties.
Key words: stars: circumstellar matter / stars: planetary systems: protoplanetary disks
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


