| Issue |
A&A
Volume 506, Number 2, November I 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L1 - L4 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200912787 | |
| Published online | 15 September 2009 | |
Letter to the Editor
Empirical estimate of Lyα escape fraction in a statistical sample of Lyα emitters
1
Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris (IAP), 98bis boulevard Arago, 75014 Paris, France e-mail: atek@iap.fr
2
Observatoire de Genève, Université de Genève, 51 Ch. des Maillettes, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
3
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Toulouse-Tarbes, Université de Toulouse, CNRS, 14 Avenue E. Belin, 31400 Toulouse, France
4
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille, UMR 6110 CNRS/Université de Provence, 38 rue Joliot-Curie, 13388 Marseille Cedex 13, France
5
Oskar Klein Center for Cosmoparticle physics, Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, 10691 Stockholm, Sweden
6
Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA), POB 78, E28691 Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain
Received:
29
June
2009
Accepted:
8
September
2009
Context. The Lyman-alpha (Lyα) recombination line is a fundamental tool for galaxy evolution studies and modern observational cosmology. However, subsequent interpretations are still prone to a number of uncertainties. Besides numerical efforts, empirical data are urgently needed for a better understanding of the Lyα escape process.
Aims. We empirically estimate the Lyα escape fraction in a statistically significant sample of galaxies in a redshift range z ~ 0 - 0.3. This estimate will constrain interpretations of current high-redshift Lyα observations.
Methods. An optical spectroscopic follow-up of a sub-sample of 24 Lyα emitters detected by GALEX at z ~ 0.2 - 0.3, combined with a UV-optical sample of local starbursts, both with matched apertures, allow us to quantify the dust extinction through Balmer lines, and to estimate the Lyα escape fraction from the Hα flux corrected for extinction in the framework of the recombination theory.
Results. The global escape fraction of Lyα radiation spans a wide range of values and 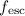 (Lyα)
clearly decreases with increasing nebular dust extinction
(Lyα)
clearly decreases with increasing nebular dust extinction 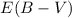 .
Several objects show
.
Several objects show 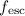 (Lyα) greater than
(Lyα) greater than 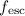 (continuum), which may be taken as observational evidence for a clumpy ISM geometry or for
an aspherical ISM.
Selection biases and aperture size effects may still prevail between
z ~ 0.2 - 0.3 Lyman-alpha emitters (LAEs) and local starbursts and may explain the difference observed for
(continuum), which may be taken as observational evidence for a clumpy ISM geometry or for
an aspherical ISM.
Selection biases and aperture size effects may still prevail between
z ~ 0.2 - 0.3 Lyman-alpha emitters (LAEs) and local starbursts and may explain the difference observed for 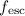 (Lyα).
(Lyα).
Key words: galaxies: starburst / galaxies: ISM / ultraviolet: galaxies / ISM: dust, extinction
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


