| Issue |
A&A
Volume 505, Number 1, October I 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 417 - 439 | |
| Section | Catalogs and data | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200912111 | |
| Published online | 11 August 2009 | |
The second INTEGRAL AGN catalogue*
1
ISDC Data Centre for Astrophysics, Chemin d'Écogia 16, 1290 Versoix, Switzerland e-mail: beckmann@apc.univ-paris7.fr
2
Observatoire Astronomique de l'Université de Genève, Chemin des Maillettes 51, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
3
APC Laboratory, Université Paris Diderot, 10 rue A. Domon et L. Duquet, 75205 Paris Cedex 13, France
4
Laboratoire AIM – CNRS – CEA/DSM – Université Paris Diderot (UMR 7158), CEA Saclay, DSM/IRFU/SAp, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
5
Centro de Astrobiología LAEX (CSIC-INTA), POB 78, 28691 Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain
6
Astrophysics Science Division, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Code 661, MD 20771, USA
7
Centrum Astronomiczne im. M. Kopernika, Bartycka 18, 00-716 Warszawa, Poland
Received:
19
March
2009
Accepted:
30
June
2009
Aims. The INTEGRAL mission provides a large data set for studying the hard X-ray properties of AGN and allows testing of the unified scheme for AGN.
Methods. We present analysis of INTEGRAL IBIS/ISGRI, JEM-X, and OMC data for 199 AGN supposedly detected by INTEGRAL above 20 keV.
Results. The data analysed here allow significant spectral extraction on 148 objects and an optical variability study of 57 AGN. The slopes of the hard X-ray spectra of Seyfert 1 and Seyfert 2 galaxies are found to be consistent within the uncertainties, whereas higher cut-off energies and lower luminosities we measured for the more absorbed/type 2 AGN. The intermediate Seyfert 1.5 objects exhibit hard X-ray spectra consistent with those of Seyfert 1. When applying a Compton reflection model, the underlying continua appear the same in Seyfert 1 and 2 with Γ 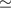 2, and the reflection strength is about R
2, and the reflection strength is about R 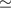 1, when assuming different inclination angles. A significant correlation is found between the hard X-ray and optical luminosity and the mass of the central black hole in the sense that the more luminous objects appear to be more massive. There is also a general trend toward the absorbed sources and type 2 AGN having lower Eddington ratios. The black hole mass appears to form a fundamental plane together with the optical and X-ray luminosity of the form
1, when assuming different inclination angles. A significant correlation is found between the hard X-ray and optical luminosity and the mass of the central black hole in the sense that the more luminous objects appear to be more massive. There is also a general trend toward the absorbed sources and type 2 AGN having lower Eddington ratios. The black hole mass appears to form a fundamental plane together with the optical and X-ray luminosity of the form 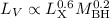 , similar to what is found between
, similar to what is found between 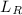 , LX, and MBH.
, LX, and MBH.
Conclusions. The transition from the type 1 to type 2 AGN appears to be smooth. The type 2 AGN are less luminous and have less accreting super massive black holes. The unified model for Seyfert galaxies seems to hold, showing in hard X-rays that the central engine is the same in Seyfert 1 and 2, but seen under different inclination angles and absorption. The fundamental plane links the accretion mechanism with the bulge of the host galaxy and with the mass of the central engine in the same way in all types of Seyfert galaxies.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: Seyfert / X-rays: galaxies / surveys / catalogs
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


