| Issue |
A&A
Volume 501, Number 3, July III 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1047 - 1058 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200911816 | |
| Published online | 27 May 2009 | |
Broad-band properties of the hard X-ray cataclysmic variables IGR J00234+6141 and 1RXS J213344.1+510725*
1
Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Padova, vicolo dell'Osservatorio 3, 35122 Padova, Italy e-mail: gabriele.anzolin@unipd.it
2
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, salita Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy e-mail: demartino@oacn.inaf.it
3
CEA Saclay, DSM/DAPNIA/Service d'Astrophysique, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France e-mail: [mfalanga;bonnetbidaud]@cea.fr
4
CRESST and X-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA and Department of Physics, University of Maryland, Baltimore County, 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250, USA e-mail: koji.mukai@nasa.gov
5
Laboratoire APC, Université Denis Diderot, 10 rue Alice Domon et Léonie Duquet, 75005 Paris, France and LUTH, Observatoire de Paris, Section de Meudon, 5 place Jules Janssen, 92195 Meudon, France e-mail: martine.mouchet@obspm.fr
6
Department of physics, Saitama University, Saitama, Japan e-mail: terada@phy.saitama-u.ac.jp
7
Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, 3-1-1, Yoshinodai, Sagamihara, Kanagawa 229-8150, Japan e-mail: ishida@astro.isas.jaxa.jp
Received:
9
February
2009
Accepted:
25
April
2009
Context. A significant number of cataclysmic variables have been detected as hard X-ray sources in the INTEGRAL survey, most of them of the magnetic intermediate polar type.
Aims. We present a detailed X-ray broad-band study of two new sources, IGR J00234+6141 and 1RXS J213344.1+510725, that allow us to classify them as secure members of the intermediate polar class.
Methods. Timing and spectral analysis of IGR J00234+6141 are based on an XMM-Newton observation and INTEGRAL publicly available data. For 1RXS J213344.1+510725, we use XMM-Newton and Suzaku observations at different epochs, as well as INTEGRAL publicly available data.
Results. We determine a spin period of 561.64 ± 0.56 s for the white dwarf in IGR J00234+6141. The X-ray pulses are observed up to 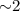 keV. From XMM-Newton and Suzaku observations of 1RXS J213344.1+510725, we find a rotational period of 570.862 ± 0.034 s. The observations span three epochs where the pulsation is observed to change at different energies both in amplitude and shape. In both objects, the spectral analysis spanned over a wide energy range, from 0.3 to 100 keV, shows the presence of multiple emission components absorbed by dense material. The X-ray spectrum of IGR J00234+6141 is consistent with a multi-temperature plasma with a maximum temperature of
keV. From XMM-Newton and Suzaku observations of 1RXS J213344.1+510725, we find a rotational period of 570.862 ± 0.034 s. The observations span three epochs where the pulsation is observed to change at different energies both in amplitude and shape. In both objects, the spectral analysis spanned over a wide energy range, from 0.3 to 100 keV, shows the presence of multiple emission components absorbed by dense material. The X-ray spectrum of IGR J00234+6141 is consistent with a multi-temperature plasma with a maximum temperature of 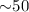 keV. In 1RXS J213344.1+510725, multiple optically thin components are inferred, as well as an optically thick (blackbody) soft X-ray emission with a temperature of
keV. In 1RXS J213344.1+510725, multiple optically thin components are inferred, as well as an optically thick (blackbody) soft X-ray emission with a temperature of 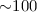 eV.
This adds 1RXS J213344.1+510725 to the growing group of soft X-ray intermediate polars.
eV.
This adds 1RXS J213344.1+510725 to the growing group of soft X-ray intermediate polars.
Conclusions. Though showing similar rotational periods and being hard X-ray sources, these two intermediate polars appear different in several respects, among which the presence of a soft X-ray component in 1RXS J213344.1+510725. This source also emits circularly polarized light in the optical band, thus joining the group of soft and polarized intermediate polars as a fifth member. How the hard X-ray and polarized emission are thermalized in these systems is a timely question.
Key words: stars: binaries: close / stars: individual: IGR J00234+6141 / stars: individual: 1RXS J213344.1+510725 / stars: novae, cataclysmic variables / X-rays: stars / accretion, accretion disks
Based on observations obtained with XMM-Newton and INTEGRAL, ESA science missions with instruments and contributions directly funded by ESA Member States and NASA, and with Suzaku, a Japan's mission developed at the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency in collaboration with US (NASA/GSFC, MIT) and Japanese institutions.
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


