| Issue |
A&A
Volume 499, Number 1, May III 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 267 - 272 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/200811041 | |
| Published online | 27 March 2009 | |
The isolated neutron star RBS1774 revisited *,**
Revised XMM-Newton X-ray parameters and an optical counterpart from deep LBT-observations
1
Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany e-mail: aschwope@aip.de
2
Argelander-Institut für Astronomie (AIfA), University of Bonn, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany
3
Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721, USA
4
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy
5
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via di Frascati 33, 00040 Monteporzio, Italy
6
INAF – Osservatorio di Padova, vicolo dell'Osservatorio 5, 35122 Padova, Italy
Received:
26
September
2008
Accepted:
18
February
2009
We report optical B-band observations with the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT) of the isolated neutron star RBS1774. The stacked image with a total exposure of 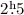 reveals a candidate optical counterpart at mB = 26.96 ± 0.20 at position
reveals a candidate optical counterpart at mB = 26.96 ± 0.20 at position 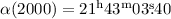 ,
, 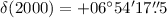 , within the joint Chandra and
XMM-Newton error circles. We analyse archival XMM-Newton observations and derive revised spectral and positional parameters. The predicted optical flux from the extrapolated X-ray spectrum is likely twice as high as reported before. The measured optical flux exceeds the extrapolated X-ray spectral flux by a factor
, within the joint Chandra and
XMM-Newton error circles. We analyse archival XMM-Newton observations and derive revised spectral and positional parameters. The predicted optical flux from the extrapolated X-ray spectrum is likely twice as high as reported before. The measured optical flux exceeds the extrapolated X-ray spectral flux by a factor 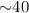 (15-60 at 1σ confidence). We interpret our detection and the
spectral energy distribution as further evidence of a temperature structure over the neutron star's surface and present a pure thermal model reflecting both the SED and the pulsed fraction of the light curve.
(15-60 at 1σ confidence). We interpret our detection and the
spectral energy distribution as further evidence of a temperature structure over the neutron star's surface and present a pure thermal model reflecting both the SED and the pulsed fraction of the light curve.
Key words: X-rays: stars / stars: neutron / stars: individual: RBS1774
Based on observations obtained with XMM-Newton, an ESA science mission with instruments and contributions directly funded by ESA Member States and NASA.
Based on data acquired using the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT). The LBT is an international collaboration among institutions in the US, Italy, and Germany. LBT Corporation partners are the University of Arizona, on behalf of the Arizona university system; Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica, Italy; LBT Beteiligungsgesellschaft, Germany, representing the Max Planck Society, the Astrophysical Institute Potsdam, and Heidelberg University; Ohio State University; and the Research Corporation, on behalf of the University of Notre Dame, the University of Minnesota, and the University of Virginia.
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


