| Issue |
A&A
Volume 494, Number 2, February I 2009
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 539 - 551 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200811212 | |
| Published online | 04 December 2008 | |
The mass function of young star clusters in spiral galaxies
Astronomical Institute, University of Utrecht, Princetonplein 5, 3584 CC Utrecht, The Netherlands e-mail: S.S.Larsen@uu.nl
Received:
22
October
2008
Accepted:
20
November
2008
Aims. The initial cluster mass function (ICMF) in spiral discs is constrained and compared with data for old globular clusters and young clusters in starbursts.
Methods. For a given absolute magnitude, the cluster age distribution depends on the ICMF. Here, the behaviour of the median age-magnitude relation is analysed in detail for Schechter ICMFs with various cut-off masses, Mc. The calculated relations are compared with observations of the brightest clusters in spiral galaxies. Schechter functions are also fitted directly to observed mass functions (MFs).
Results. A single Schechter ICMF with an Mc of a few times 105 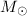 can reproduce the observed ages and luminosities of the brightest (and 5th brightest) clusters in the spirals if disruption of optically visible clusters is dominated by relatively slow secular evolution. A Schechter function fit to the combined cluster MF for all spirals in the sample yields Mc = (2.1±0.4)
can reproduce the observed ages and luminosities of the brightest (and 5th brightest) clusters in the spirals if disruption of optically visible clusters is dominated by relatively slow secular evolution. A Schechter function fit to the combined cluster MF for all spirals in the sample yields Mc = (2.1±0.4) 105
105 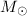 . The MFs in cluster-poor and cluster-rich spirals are statistically indistinguishable. An Mc = 2.1
. The MFs in cluster-poor and cluster-rich spirals are statistically indistinguishable. An Mc = 2.1 105
105 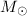 Schechter function also fits the MF of young clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud. If the same ICMF applies in the Milky Way, a bound cluster with M > 105
Schechter function also fits the MF of young clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud. If the same ICMF applies in the Milky Way, a bound cluster with M > 105 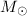 will form about once every 107 years, while an M > 106
will form about once every 107 years, while an M > 106 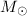 cluster will form only once every 50 Gyr. Luminosity functions (LFs) of model cluster populations drawn from an Mc = 2.1
cluster will form only once every 50 Gyr. Luminosity functions (LFs) of model cluster populations drawn from an Mc = 2.1 105
105 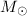 Schechter ICMF generally agree with LFs observed in spiral galaxies.
Schechter ICMF generally agree with LFs observed in spiral galaxies.
Conclusions.
The ICMF in present-day spiral discs can be modelled as a Schechter function with Mc ≈ 2 105
105 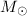 . However, the presence of significant numbers of M > 106
. However, the presence of significant numbers of M > 106 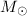 (and even M > 107
(and even M > 107 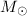 ) clusters in some starburst galaxies makes it unlikely that the Mc value derived for spirals is universal. In high-pressure environments, such as those created by complex gas kinematics and feedback in mergers, Mc can shift to higher masses than in quiescent discs.
) clusters in some starburst galaxies makes it unlikely that the Mc value derived for spirals is universal. In high-pressure environments, such as those created by complex gas kinematics and feedback in mergers, Mc can shift to higher masses than in quiescent discs.
Key words: Galaxy: open clusters and associations: general / galaxies: star clusters / galaxies: spiral
© ESO, 2009
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


