| Issue |
A&A
Volume 490, Number 2, November I 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 807 - 810 | |
| Section | Stellar atmospheres | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200810627 | |
| Published online | 17 September 2008 | |
Research Note
Determining parameters of cool giant stars by modeling spectrophotometric and interferometric observations using the SAtlas program
1
Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Canada e-mail: neilson@astro.utoronto.ca
2
Department of Chemical and Physical Sciences, University of Toronto Mississauga, Canada e-mail: lester@astro.utoronto.ca
Received:
16
July
2008
Accepted:
12
September
2008
Context. Optical interferometry is a powerful tool for observing the intensity structure and angular diameter of stars. When combined with spectroscopy and/or spectrophotometry, interferometry provides a powerful constraint for model stellar atmospheres.
Aims. The purpose of this work is to test the robustness of the spherically symmetric version of the Atlas stellar atmosphere program, SAtlas, using interferometric and spectrophotometric observations.
Methods. Cubes (three dimensional grids) of model stellar atmospheres, with dimensions of luminosity, mass, and radius, are computed to fit observations for three evolved giant stars, ψ Phoenicis, γ Sagittae, and α Ceti. The best-fit parameters are compared with previous results.
Results. The best-fit angular diameters and values of 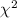 are consistent with predictions using Phoenix and plane-parallel Atlas models. The predicted effective temperatures, using SAtlas, are about 100 to 200
are consistent with predictions using Phoenix and plane-parallel Atlas models. The predicted effective temperatures, using SAtlas, are about 100 to 200  lower, and the predicted luminosities are also lower due to the differences in effective temperatures.
lower, and the predicted luminosities are also lower due to the differences in effective temperatures.
Conclusions. It is shown that the SAtlas program is a robust tool for computing models of extended stellar atmospheres that are consistent with observations. The best-fit parameters are consistent with predictions using Phoenix models, and the fit to the interferometric data for ψ Phe differs slightly, although both agree within the uncertainty of the interferometric observations.
Key words: stars: atmospheres / stars: fundamental parameters / stars: late-type
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


