| Issue |
A&A
Volume 486, Number 3, August II 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 683 - 695 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078878 | |
| Published online | 04 June 2008 | |
The Vimos VLT deep survey
Global properties of 20 000 galaxies in the IAB < 22.5 WIDE survey
1
INAF-IASF, via Bassini 15, 20133, Milano, Italy e-mail: bianca@lambrate.inaf.it
2
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille, UMR 6110 CNRS-Université de Provence, BP8, 13376 Marseille Cedex 12, France
3
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Brera, via Brera 28, 20021, Milan, Italy
4
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127, Bologna, Italy
5
INAF-IRA, via Gobetti 101, 40129, Bologna, Italy
6
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via di Frascati 33, 00040, Monte Porzio Catone, Italy
7
Canada France Hawaii Telescope corporation, Mamalahoa Hwy, Kamuela, HI-96743, USA
8
Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik, 85741, Garching, Germany
9
Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, UMR 7095, 98 bis Bvd Arago, 75014, Paris, France
10
Laboratoire d' Astrophysique de Toulouse-Tarbes, Université de Toulouse, CNRS, 14 avenue Edouard Belin, 31400 Toulouse, France
11
Max Planck Institut für Extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Giessenbachstrasse 1, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany
12
Astrophysical Institute Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482, Potsdam, Germany
13
School of Physics & Astronomy, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, NG72RD, UK
14
Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Avenue de l'Observatoire, 75014, Paris, France
15
Università di Bologna, Dipartimento di Astronomia, via Ranzani 1, 40127, Bologna, Italy
16
Centre de Physique Théorique, UMR 6207 CNRS-Université de Provence, 13288, Marseille, France
17
Integral Science Data Centre, ch. d'Écogia 16, 1290, Versoix, Switzerland
18
Geneva Observatory, ch. des Maillettes 51, 1290, Sauverny, Switzerland
19
Astronomical Observatory of the Jagiellonian University, ul Orla 171, 30-244, Kraków, Poland
20
The Andrzej Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Hoza 69, 00-681 Warsaw, Poland
21
INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, via Moiariello 16, 80131, Napoli, Italy
22
Université de Lyon, Lyon, 69003, France; Université Lyon 1, Observatoire de Lyon, 9 avenue Charles André, Saint-Genis Laval, 69230; CNRS, UMR 5574, Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon; École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon, 69007, France
23
Universitá di Milano-Bicocca, Dipartimento di Fisica, Piazza delle Scienze 3, 20126, Milano, Italy
Received:
19
October
2007
Accepted:
24
April
2008
Context. The VVDS-Wide survey has been designed to trace
the large-scale distribution of galaxies at z ~ 1 on comoving scales reaching
~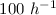 Mpc, while providing a good control of cosmic variance
over areas as large as a few square degrees. This is achieved by measuring
redshifts with VIMOS at the ESO VLT to a limiting magnitude
IAB = 22.5, targeting four independent fields with sizes of up to 4 deg2 each.
Mpc, while providing a good control of cosmic variance
over areas as large as a few square degrees. This is achieved by measuring
redshifts with VIMOS at the ESO VLT to a limiting magnitude
IAB = 22.5, targeting four independent fields with sizes of up to 4 deg2 each.
Aims. We discuss the survey strategy which covers 8.6 deg2 and present the general properties of the current redshift sample. This includes 32 734 spectra in the four regions, covering a
total area of 6.1 deg2 with a sampling rate of 22 to 24%. This
paper accompanies the public release of the first 18 143 redshifts of
the VVDS-Wide survey from the 4 deg2 contiguous area of the F22 field at RA = 22 .
.
Methods. We have devised and tested an objective method to assess the quality of each spectrum, providing a compact figure-of-merit. This is particularly effective in the case of long-lasting spectroscopic surveys with varying observing conditions. Our figure of merit is a measure of the robustness of the redshift measurement and, most importantly, can be used to select galaxies with uniform high-quality spectra to carry out reliable measurements of spectral features. We also use the data available over the four independent regions to directly measure the variance in galaxy counts. We compare it with general predictions from the observed galaxy two-point correlation function at different redshifts and with that measured in mock galaxy surveys built from the Millennium simulation.
Results. The purely magnitude-limited VVDS Wide sample includes 19 977 galaxies, 304 type I AGNs, and 9913 stars. The redshift success rate is above 90%
independent of magnitude. A cone diagram of the galaxy spatial distribution provides us with the
current largest overview of large-scale structure up to z ~ 1,
showing a rich texture of over- and under-dense regions.
We give the mean 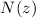 distribution averaged over 6.1 deg2 for a sample limited in magnitude to IAB = 22.5. Comparing galaxy densities from the four fields
shows that in a redshift bin Δz = 0.1 at z ~ 1 one
still has factor-of-two variations over areas as large as ~ 0.25 deg2. This level of cosmic variance agrees with that obtained by integrating the galaxy two-point correlation function estimated from the F22 field alone. It is also in fairly good statistical agreement
with that predicted by the Millennium simulations.
distribution averaged over 6.1 deg2 for a sample limited in magnitude to IAB = 22.5. Comparing galaxy densities from the four fields
shows that in a redshift bin Δz = 0.1 at z ~ 1 one
still has factor-of-two variations over areas as large as ~ 0.25 deg2. This level of cosmic variance agrees with that obtained by integrating the galaxy two-point correlation function estimated from the F22 field alone. It is also in fairly good statistical agreement
with that predicted by the Millennium simulations.
Conclusions. The VVDS WIDE survey currently provides the largest area coverage among redshift surveys reaching z ~ 1. The variance estimated over the survey fields shows explicitly how clustering results from deep surveys of even 1 deg2 size should be interpreted with caution. The survey data represent a rich data base to select complete sub-samples of high-quality spectra and to study galaxy ensemble properties and galaxy clustering over unprecedented scales at these redshifts. The redshift catalog of the 4 deg2 F22 field is publicly available at http://cencosw.oamp.fr.
Key words: galaxies: fundamental parameters / cosmology: observations / cosmology: large-scale structure of Universe / catalogs
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


