| Issue |
A&A
Volume 484, Number 1, June II 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 17 - 28 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078819 | |
| Published online | 19 March 2008 | |
Three-fluid plasmas in star formation
II. Momentum transfer rate coefficients
1
Dipartimento di Astronomia e Scienza dello Spazio, Università di Firenze, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125 Firenze, Italy e-mail: cecilia@arcetri.astro.it
2
INAF – Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri, Largo E. Fermi 5, 50125 Firenze, Italy
Received:
9
October
2007
Accepted:
16
February
2008
Context. The charged component of the insterstellar medium consists of atomic and molecular ions, electrons, and charged dust grains, coupled to the local Galactic magnetic field. Collisions between neutral particles (mostly atomic or molecular hydrogen) and charged species, and between the charged species themselves, affect the magnetohydrodynamical behaviour of the medium and the dissipation of electric currents.
Aims. The friction force due to elastic collisions between particles of different species in the multi-component interstellar plasma is a nonlinear function of the temperature of each species and the Mach number of the relative drift velocity. The aim of this paper is to provide an accurate and, as far as possible, complete set of momentum transfer rate coefficients for magnetohydrodynamical studies of the interstellar medium.
Methods. Momentum transfer rates are derived from available experimental data and theoretical calculations of cross sections within the classic approach developed by Boltzmann and Langevin for a wide range of values of the temperature and the drift velocity.
Results. Accurate numerical values for momentum transfer rates are obtained and
fitted to simple analytical formulae expressing the dependence of the
results on the gas temperature and the relative drift velocity.
The often used polarization approximation is in satisfactory agreement
with our results only for collisions between H2 and molecular ions (HCO+, H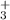 ). For other kinds of collisions, the polarization approximation fails by large factors, and must be replaced by
more accurate expressions.
). For other kinds of collisions, the polarization approximation fails by large factors, and must be replaced by
more accurate expressions.
Key words: atomic processes / molecular processes / plasmas / magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) / ISM: clouds / ISM: jets and outflows
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


