| Issue |
A&A
Volume 481, Number 3, April III 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 771 - 776 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20079335 | |
| Published online | 18 February 2008 | |
Soft X-ray spectral variability of AM Herculis*
1
Institut für Astrophysik, Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany e-mail: [beuermann;reinsch]@astro.physik.uni-goettingen.de
2
National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics, Helwan, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: essam@nriag.sci.eg
Received:
27
December
2007
Accepted:
7
February
2008
Context. Polars (AM Herculis binaries) are a prominent class of bright soft X-ray sources, many of which were discovered with ROSAT.
Aims. We present a homogenous analysis of all the pointed ROSAT PSPC observations of polars subdivided into two papers that discuss the prototype polar AM Her in detail and summarize the class properties of all other polars.
Methods. We derive the high-state soft X-ray flux and short-term spectral variability of AM Her using a new detector response matrix and a confirmed flux calibration of the ROSAT PSPC below 0.28 keV.
Results.
The best-fit mean single-blackbody temperature and integrated
bright-phase energy flux of AM Her in its April 1991 high state are
 eV and
eV and 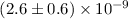 erg cm-2 s-1, respectively. The
total blackbody flux of a multi-temperature model that fits both the soft
X-ray and the fluctuating far-ultraviolet components is
erg cm-2 s-1, respectively. The
total blackbody flux of a multi-temperature model that fits both the soft
X-ray and the fluctuating far-ultraviolet components is
 erg cm-2 s-1. The total accretion
luminosity at a distance of 80 pc,
erg cm-2 s-1. The total accretion
luminosity at a distance of 80 pc,
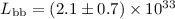 erg s-1, implies an accretion rate of
erg s-1, implies an accretion rate of
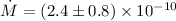
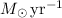 for an 0.78
for an 0.78  white
dwarf. The soft X-ray flux displays significant variability on time
scales down to 200 ms. Correlated spectral and count-rate variations
are seen in flares on time scales down to 1 s, demonstrating the
heating and cooling associated with individual accretion events.
white
dwarf. The soft X-ray flux displays significant variability on time
scales down to 200 ms. Correlated spectral and count-rate variations
are seen in flares on time scales down to 1 s, demonstrating the
heating and cooling associated with individual accretion events.
Conclusions. Our spectral and temporal analysis provides direct evidence for the blobby accretion model and suggests a connection between the soft X-ray and the fluctuating far-ultraviolet components.
Key words: accretion, accretion disks / methods: data analysis / stars: novae, cataclysmic variables / stars: individual: AM Her / X-rays: binaries
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


