| Issue |
A&A
Volume 481, Number 1, April I 2008
Science with Hinode
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 117 - 122 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078906 | |
| Published online | 25 January 2008 | |
Broad Lyα emission from supernova remnants in young galaxies *
1
Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strae 1, 85740 Garching, Germany e-mail: heng@ias.edu
2
Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrae, 85478 Garching, Germany
3
Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Profsoyuznaya 84/32, 117997 Moscow, Russia
Received:
23
October
2007
Accepted:
18
December
2007
Context.Charge transfer (or exchange) reactions between hydrogen atoms and protons in collisionless shocks of supernova remnants (SNRs) are a natural way of producing broad Balmer, Lyman, and other lines of hydrogen.
Aims.We wish to quantify the importance of shock-induced, non-thermal hydrogen emission from SNRs in young galaxies.
Methods.We present a method estimating the luminosity of broad (~1000 km s-1) Lyα, Lyβ, Lyγ, Hβ and Pα lines, as well as the broad and narrow luminosities of the two-photon (2γ) continuum, from existing measurements of the Hα flux. We consider cases of 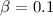 and 1, where
and 1, where 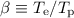 is the ratio of electron-to-proton temperatures. We examine a modest sample of 8 proximate, Balmer-dominated SNRs from our Galaxy and the Large Magellanic Cloud. The expected broad Lyα luminosity per object is at most ~1036 erg s-1. The 2γ continuum luminosities are comparable to the broad Hα and Lyα ones. We restrict our analysis to homogenous and static media.
is the ratio of electron-to-proton temperatures. We examine a modest sample of 8 proximate, Balmer-dominated SNRs from our Galaxy and the Large Magellanic Cloud. The expected broad Lyα luminosity per object is at most ~1036 erg s-1. The 2γ continuum luminosities are comparable to the broad Hα and Lyα ones. We restrict our analysis to homogenous and static media.
Results.Differences in the Lyα/Hα and Lyβ/Hα
luminosity ratios between the 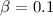 and 1 cases are factors
~2 for shock velocities
and 1 cases are factors
~2 for shock velocities 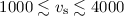 km s-1, thereby providing a direct and unique way to
measure β. In principle, broad, “non-radiative” Lyα
from SNRs in young galaxies can be directly observed in the optical
range of wavelengths. However, by taking the
different rates between core collapse and thermonuclear
supernovae into consideration, as well as the duration we expect to observe such Lyα emission from SNRs, we expect their
contribution to the total Lyα luminosity from
km s-1, thereby providing a direct and unique way to
measure β. In principle, broad, “non-radiative” Lyα
from SNRs in young galaxies can be directly observed in the optical
range of wavelengths. However, by taking the
different rates between core collapse and thermonuclear
supernovae into consideration, as well as the duration we expect to observe such Lyα emission from SNRs, we expect their
contribution to the total Lyα luminosity from 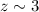 to 5 galaxies to be negligibly small (~0.001%),
compared to the radiative shock mechanism described by Shull & Silk (1979). Although broad, non-thermal Lyα emission has never been observed, these photons are produced in SNRs. Hence, the non-radiative Lyα luminosity is a part of the intrinsic Lyα spectrum of young galaxies.
to 5 galaxies to be negligibly small (~0.001%),
compared to the radiative shock mechanism described by Shull & Silk (1979). Although broad, non-thermal Lyα emission has never been observed, these photons are produced in SNRs. Hence, the non-radiative Lyα luminosity is a part of the intrinsic Lyα spectrum of young galaxies.
Key words: ISM: supernova remnants / atomic processes / radiation mechanisms: general / galaxies: general
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


