| Issue |
A&A
Volume 480, Number 3, March IV 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 723 - 733 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078439 | |
| Published online | 18 December 2007 | |
Microlensing constraints on the Galactic bulge initial mass function
1
Dipartimento di Fisica “E. R. Caianiello”, Università di Salerno, via S. Allende, 84081 Baronissi (SA), Italy e-mail: novati@sa.infn.it
2
Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, sezione di Napoli, Italy
3
Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Zürich, Winterthurerstrasse 190, 8057 Zürich, Switzerland
Received:
7
August
2007
Accepted:
16
November
2007
Aims.We seek to probe the Galactic bulge IMF starting from microlensing observations.
Methods.We analyse the recent results of the microlensing
campaigns carried out towards the Galactic bulge presented
by the EROS, MACHO and OGLE collaborations. In particular,
we study the duration distribution of the events.
We assume a power law initial mass function, 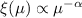 ,
and we study the slope α both in the brown dwarf
and in the main sequence ranges.
Moreover, we compare the observed and expected optical depth profiles.
,
and we study the slope α both in the brown dwarf
and in the main sequence ranges.
Moreover, we compare the observed and expected optical depth profiles.
Results.
The values of the mass function slopes are strongly
driven by the observed timescales of the microlensing events.
The analysis of the MACHO data set gives, for the main sequence stars,
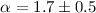 ,
compatible with the result we obtain with the EROS and OGLE data sets,
and a similar, though less constrained slope for brown dwarfs.
The lack of short duration events in both EROS and OGLE data sets, on the other hand,
only allows the determination of an upper limit in this range of masses,
making the overall result less robust.
The optical depth analysis gives a very good agreement
between the observed and the expected values,
and we show that the available data do not allow one to discriminate
between different bulge models.
,
compatible with the result we obtain with the EROS and OGLE data sets,
and a similar, though less constrained slope for brown dwarfs.
The lack of short duration events in both EROS and OGLE data sets, on the other hand,
only allows the determination of an upper limit in this range of masses,
making the overall result less robust.
The optical depth analysis gives a very good agreement
between the observed and the expected values,
and we show that the available data do not allow one to discriminate
between different bulge models.
Key words: gravitational lensing / Galaxy: bulge / Galaxy: stellar contents
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


