| Issue |
A&A
Volume 480, Number 1, March II 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 5 - 13 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078518 | |
| Published online | 02 January 2008 | |
Gamma-ray burst high energy emission from internal shocks
1
Istituto Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Sezione di Roma, INAF, via del Fosso del Cavaliere, 100-00113 Roma, Italy e-mail: alessandra.galli@iasf-roma.inaf.it
2
INFN of Trieste, Padriciano 99, 34012 Trieste, Italy
3
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Roma, via Frascati 33, 00040 Monteporzio Catone, Italy
Received:
20
August
2007
Accepted:
21
November
2007
Aims.In this paper we study synchrotron and synchrotron self Compton (SSC) emission from internal shocks (IS) during the prompt and X-ray flare phases of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). The aim is to test the IS model for the flare emission and for whether GRBs can be GeV sources.
Methods.We determine the parameters for which the IS model can account for the observed prompt and X-ray flares emission, and study the detectability of the high energy SSC emission by the AGILE and GLAST satellites.
Results.We find that the detectability of the SSC emission during the prompt phase of GRBs improves for higher values of the fireball Lorentz factor Γ and of the temporal variability tv. If IS is the mechanism responsible for the flare emission, and the Lorentz factor of the shells producing the flare is Γ ~ 100, the flare light curves are expected to present some substructures with temporal variability tv = 10-100 ms which are much smaller than the average duration of flares, and similar to those observed during the prompt phase of GRBs. If one assumes lower Lorentz factors, such as Γ ~ 10 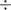 25, then a larger temporal variability tv ~ 40 s can also account for the observed flare properties. However in this case we predict that X-ray flares do not have a counterpart at very high energies (MeV–GeV).
25, then a larger temporal variability tv ~ 40 s can also account for the observed flare properties. However in this case we predict that X-ray flares do not have a counterpart at very high energies (MeV–GeV).
Conclusions.An investigation on the substructures of the X-ray flare light curves, and simultaneous X-ray and high energy observations, will allow us to corroborate the hypothesis that late IS are responsible for the X-ray flares.
Key words: radiation mechanisms: non-thermal / gamma rays: bursts
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


