| Issue |
A&A
Volume 478, Number 3, February II 2008
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 755 - 762 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078378 | |
| Published online | 12 December 2007 | |
Ground-based variability surveys towards Centaurus A: worthwhile or not?*
1
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail: dejong@mpia.de
2
Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of Groningen, PO Box 800, 9700 AV, Groningen, The Netherlands
3
Sterrewacht Leiden, University of Leiden, PO Box 9513, 2300 RA, Leiden, The Netherlands
4
Argelander Institut für Astronomie, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany
Received:
30
July
2007
Accepted:
28
November
2007
Context.Difference imaging has proven to be a powerful technique for detecting and monitoring the variability of unresolved stellar sources in M 31. Using this technique in surveys of galaxies outside the Local Group could have many interesting applications.
Aims.The goal of this paper is to test difference imaging photometry on Centaurus A, the nearest giant elliptical galaxy, at a distance of 4 Mpc.
Methods.We obtained deep photometric data with the Wide Field Imager at the ESO/MPG 2.2 m at La Silla spread over almost two months. Applying the difference imaging photometry package DIFIMPHOT, we produced high-quality difference images and detected variable sources. The sensitivity of the current observational setup was determined through artificial residual tests.
Results.In the resulting high-quality difference images, we detect 271 variable stars. We find a difference flux detection limit corresponding to mR 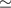 24.5. Based on a simple model of the
halo of Centaurus A, we estimate that a ground-based microlensing
survey would detect in the order of 4 microlensing events per year
due to lenses in the halo.
24.5. Based on a simple model of the
halo of Centaurus A, we estimate that a ground-based microlensing
survey would detect in the order of 4 microlensing events per year
due to lenses in the halo.
Conclusions.Difference imaging photometry works very well at the distance of Centaurus A and promises to be a useful tool for detecting and studying variable stars in galaxies outside the local group. For microlensing surveys, a higher sensitivity is needed than achieved here, which would be possible with a large ground-based telescope or space observatory with wide-field imaging capabilities.
Key words: galaxies: individual: Centaurus A / galaxies: stellar content / stars: variables: general / gravitational lensing
© ESO, 2008
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


