| Issue |
A&A
Volume 474, Number 2, November I 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 505 - 514 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20078184 | |
| Published online | 28 August 2007 | |
Spectroscopy of horizontal branch stars in NGC 6752*
Anomalous results on atmospheric parameters and masses
1
Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Padova, Vicolo dell'osservatorio 3, 35122 Padova, Italy
2
Departamento de Astronomía, Universidad de Chile, Casilla 36-D, Santiago, Chile e-mail: mbidin@das.uchile.cl
3
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching, Germany
4
INAF – Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, Vicolo dell'osservatorio 2, 35122 Padova, Italy
5
Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur, Dpt. Cassiopée, CNRS UMR 6202, BP 4229, 06304 Nice Cedex 04, France
Received:
28
June
2007
Accepted:
8
August
2007
Context.The determination of fundamental parameters for horizontal branch stars in Galactic globular clusters frequently gives puzzling results, pointing to the lack of our understanding of their atmospheric structure and the inadequate approximations by the models.
Aims.We wanted to measure effective temperatures, surface gravities, helium abundances, and masses for hot horizontal branch stars in NGC 6752 in order to compare the results with evolutionary predictions.
Methods.We used the ESO VLT-FORS2 facility to collect low-resolution spectra of 51 targets distributed along the horizontal branch. We determined atmospheric parameters, by comparison with theoretical models through standard fitting routines, and masses by basic equations.
Results.Results generally agree with
previous works, although not always with the theoretical expectations for
cooler stars (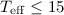 000 K). The calculated color
excess is systematically lower than the literature values, pointing
towards a possible underestimation of effective
temperatures. Moreover, we find two groups of stars at
000 K). The calculated color
excess is systematically lower than the literature values, pointing
towards a possible underestimation of effective
temperatures. Moreover, we find two groups of stars at
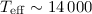 K and at
K and at  K that
present anomalies with respect to the general trend and expectations.
We suppose that the three peculiar bright stars at
K that
present anomalies with respect to the general trend and expectations.
We suppose that the three peculiar bright stars at
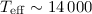 K are probably affected by an enhanced
stellar wind. For the eight extreme horizontal branch stars at
K are probably affected by an enhanced
stellar wind. For the eight extreme horizontal branch stars at
 K that show unusually high masses, we find
no plausible explanation.
K that show unusually high masses, we find
no plausible explanation.
Conclusions.While most of our results agree well with
the predictions of standard horizontal branch evolution, we still have
problems with the low masses we derive in certain temperature
ranges. We believe that Kurucz ATLAS9 LTE model atmospheres with
solar-scaled abundances are probably inadequate for these temperature
ranges. Concerning the group of anomalous stars at
 K, a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test indicates that
there is only an 8.4% probability that these stars are randomly drawn
from the general distribution in the color-magnitude diagram. This is
not conclusive but indicates that these stars could be both (and
independently) spectroscopically and photometrically peculiar with
respect to the general extreme horizontal branch population.
K, a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test indicates that
there is only an 8.4% probability that these stars are randomly drawn
from the general distribution in the color-magnitude diagram. This is
not conclusive but indicates that these stars could be both (and
independently) spectroscopically and photometrically peculiar with
respect to the general extreme horizontal branch population.
Key words: stars: horizontal-branch / stars: fundamental parameters / globular clusters: individual: NGC 6752
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


