| Issue |
A&A
Volume 471, Number 3, September I 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 813 - 824 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066361 | |
| Published online | 26 June 2007 | |
Near-infrared study of southern massive star formation regions
The case of IRAS 16571-4029 source
Resident Astronomer at Southern Astrophysical Research (SOAR) Telescope, Casilla 603, La Serena, Chile e-mail: aroman@ctio.noao.edu
Received:
7
September
2006
Accepted:
8
May
2007
Context.We present the results of a near-infrared survey of the young stellar cluster associated with the IRAS 16571-4029 source.
Aims.The main purpose of this survey is to study the cluster members and find the ionizing sources of the associated HII region.
Methods.The stellar population was studied by using color–color and color–magnitude diagrams, as well as by analysing the spectral energy distributions in the near- and mid-infrared wavelengths. The extended emission was studied by the construction of contour diagrams, which were compared with near- and mid-infrared images. We computed the corresponding number of Lyman continuum photons (using the integrated Brγ flux density) and compared it with that obtained from the 5 GHz flux density to derive a mean visual extinction.
Results.NIR observations in the direction of RCW116B reveal the presence of a young cluster
of massive stars coincident with the IRAS 16571-4029 source. These observations, together with published radio data, MSX, and Spitzer images were used to determine some of the physical
parameters of the region.
We found 102 cluster member candidates in an area of about 3  3 square arcmin, the
majority of them showing excess emission in the NIR.
We found that IRAS 16571-4029 is formed by multiple infrared sources, all but one are
associated with small groups of stars. This suggests that the fragmentation of massive molecular
clouds generates the massive sub-clusters.
We derived a mean visual extinction of
3 square arcmin, the
majority of them showing excess emission in the NIR.
We found that IRAS 16571-4029 is formed by multiple infrared sources, all but one are
associated with small groups of stars. This suggests that the fragmentation of massive molecular
clouds generates the massive sub-clusters.
We derived a mean visual extinction of 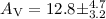 . This result is independent of
the assumed distance and agrees with the mean visual extinction
. This result is independent of
the assumed distance and agrees with the mean visual extinction 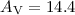 , as obtained by
previous spectroscopic observations of two NIR sources in the direction of the
IRAS 16571-4029 source.
We also compare the results obtained in this study with those obtained in previous papers in this
series finding a very good correlation between the number of cluster members Ns and the
cluster radius rc.
The cluster radius varies from 0.2-0.3 pc (IRAS 15411-5352 and IRAS 16132-5039) until about 1 pc (IRAS 15408-5356).
The youngest clusters are those associated with the RCW95 complex
(IRAS 15408-5356 and IRAS 15411-5353) with ages in the range 1.5-2
, as obtained by
previous spectroscopic observations of two NIR sources in the direction of the
IRAS 16571-4029 source.
We also compare the results obtained in this study with those obtained in previous papers in this
series finding a very good correlation between the number of cluster members Ns and the
cluster radius rc.
The cluster radius varies from 0.2-0.3 pc (IRAS 15411-5352 and IRAS 16132-5039) until about 1 pc (IRAS 15408-5356).
The youngest clusters are those associated with the RCW95 complex
(IRAS 15408-5356 and IRAS 15411-5353) with ages in the range 1.5-2  106 years, while the sources associated with the RCW106 (IRAS 16132-5039,
IRAS 16177-5018) and RCW116B (IRAS 16571-4029) complexes have ages in the range 2.5-3
106 years, while the sources associated with the RCW106 (IRAS 16132-5039,
IRAS 16177-5018) and RCW116B (IRAS 16571-4029) complexes have ages in the range 2.5-3  106 years. The oldest of them is the cluster associated with the
RCW121 region (IRAS 17149-4029), which has an estimated age of 4.2
106 years. The oldest of them is the cluster associated with the
RCW121 region (IRAS 17149-4029), which has an estimated age of 4.2  106 years.
106 years.
Key words: ISM: HII regions / stars: pre-main sequence / Galaxy: structure
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


