| Issue |
A&A
Volume 469, Number 3, July III 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 925 - 940 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20077511 | |
| Published online | 02 May 2007 | |
ACS imaging of star clusters in M 51*
I. Identification and radius distribution
1
Astronomical Institute, Utrecht University, Princetonplein 5, 3584 CC Utrecht, The Netherlands e-mail: scheepmaker@astro.uu.nl
2
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London, WC1E 6BT, UK
Received:
20
March
2007
Accepted:
23
April
2007
Context.Size measurements of young star clusters are valuable tools to put constraints on the formation and early dynamical evolution of star clusters.
Aims.We use HST/ACS observations of the spiral galaxy M 51 in F435W, F555W and F814W to select a large sample of star clusters with accurate effective radius measurements in an area covering the complete disc of M 51. We present the dataset and study the radius distribution and relations between radius, colour, arm/interarm region, galactocentric distance, mass and age.
Methods.We select a sample of 7698 (F435W), 6846 (F555W) and 5024 (F814W) slightly
resolved clusters and derive their effective radii 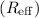 by fitting
the spatial profiles with analytical models convolved with the point
spread function. The radii of 1284 clusters are studied in detail.
by fitting
the spatial profiles with analytical models convolved with the point
spread function. The radii of 1284 clusters are studied in detail.
Results.We find cluster radii between 0.5 and ~10 pc, and one
exceptionally large cluster candidate with Reff = 21.6 pc. The median
Reff is 2.1 pc. We find 70 clusters in our sample which have colours
consistent with being old GC candidates and we find 6 new “faint
fuzzy” clusters in, or projected onto, the disc of M 51. The radius
distribution can not be fitted with a power law similar to the one for
star-forming clouds. We find an increase in Reff with colour as well
as a higher fraction of clusters with  0.05 in the
interarm regions. We find a correlation between Reff and
galactocentric distance
0.05 in the
interarm regions. We find a correlation between Reff and
galactocentric distance 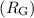 of the form Reff, which is considerably weaker than the
observed correlation for old Milky Way GCs. We find weak
relations between cluster luminosity and radius: Reff for the interarm regions and Reff for the spiral arm regions, but we do not observe a
correlation between cluster mass and radius.
of the form Reff, which is considerably weaker than the
observed correlation for old Milky Way GCs. We find weak
relations between cluster luminosity and radius: Reff for the interarm regions and Reff for the spiral arm regions, but we do not observe a
correlation between cluster mass and radius.
Conclusions.The observed radius distribution indicates that shortly after the formation of the clusters from a fractal gas, the radii of the clusters have changed in a non-uniform way. We find tentative evidence suggesting that clusters in spiral arms are more compact.
Key words: galaxies: individual: M 51 / galaxies: star clusters
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


