| Issue |
A&A
Volume 468, Number 3, June IV 2007
Extended baselines for the IRAM Plateau de Bure interferometer: First results
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 903 - 917 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066165 | |
| Published online | 11 April 2007 | |
Kinematic modelling of disk galaxies*
II. A case-study of symmetrically warped galaxy disks
Argelander Institute for Astronomy (AIfA), Univ. Bonn, Auf dem Hügel 71, 53121 Bonn, Germany e-mail: gjozsa@astro.uni-bonn.de
Received:
2
August
2006
Accepted:
2
March
2007
This is the second of a series of papers in which the kinematics
of disk galaxies is studied by analysing spectroscopic data. Making
use of the methods presented in Paper I, this work focuses on the
large-scale distribution of disk and Dark Matter halo material by analysing
the structure of warped galaxies.
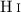 observations of three disk galaxies showing regular
large-scale (“grand-design”) warps are presented and their
structure is analysed.
The kinematics and geometry of the galaxies are modelled by fitting
a tilted-ring model directly to the data cube, thereby avoiding
problems due to orbit crowding or beam smearing.
The galaxies follow the previously known “rules for the
behaviour of warps”. Furthermore, at large radii the
observations of three disk galaxies showing regular
large-scale (“grand-design”) warps are presented and their
structure is analysed.
The kinematics and geometry of the galaxies are modelled by fitting
a tilted-ring model directly to the data cube, thereby avoiding
problems due to orbit crowding or beam smearing.
The galaxies follow the previously known “rules for the
behaviour of warps”. Furthermore, at large radii the 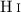 disk settles into a relatively coplanar disk that is inclined with
respect to the inner one. With increasing radius, the measured rotation velocity shows a rise. In one
of the cases, NGC 5204, the rotation curve shows a jump at the
transition radius. While the best fits in the other two cases also
suggest that such a jump is present, the change in rotation velocity is
compatible with a gradual rise. In two
cases, the surface density of the warped
disk settles into a relatively coplanar disk that is inclined with
respect to the inner one. With increasing radius, the measured rotation velocity shows a rise. In one
of the cases, NGC 5204, the rotation curve shows a jump at the
transition radius. While the best fits in the other two cases also
suggest that such a jump is present, the change in rotation velocity is
compatible with a gradual rise. In two
cases, the surface density of the warped 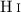 layer shows a
clear drop at the transition radius and decreases only very slowly
further out, while this feature is not as clear for UGC 3580.
A literature search shows that these properties are shared by a
number of other galaxies. In all cases, an additional, slowly
rotating gas layer is found to be present.
The change in the rotation velocity and the remarkable geometry of the disks together
indicate that the radius at which the warp starts marks the
transition between two dynamical regimes, an inner one governed by
the stellar disk and an outer one determined by the Dark Matter
halo.
layer shows a
clear drop at the transition radius and decreases only very slowly
further out, while this feature is not as clear for UGC 3580.
A literature search shows that these properties are shared by a
number of other galaxies. In all cases, an additional, slowly
rotating gas layer is found to be present.
The change in the rotation velocity and the remarkable geometry of the disks together
indicate that the radius at which the warp starts marks the
transition between two dynamical regimes, an inner one governed by
the stellar disk and an outer one determined by the Dark Matter
halo.
Key words: galaxies: kinematics and dynamics / galaxies: structure / galaxies: individual: NGC 2541 / galaxies: individual: UGC 3580 / galaxies: individual: NGC 5204
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


