| Issue |
A&A
Volume 468, Number 1, June II 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 129 - 137 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066370 | |
| Published online | 26 March 2007 | |
Searching for hidden AGN in nearby star-forming galaxies with Chandra
Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics, National Observatory of Athens, I. Metaxa & V. Pavlou, Penteli 15236, Greece e-mail: pana@astro.noa.gr
Received:
8
September
2006
Accepted:
17
March
2007
Aims. We searched for X-ray signatures of AGN in a sample of star-forming, relatively early-type, nearby spiral galaxies, from the optical spectroscopic sample of Ho et al. The tight correlations between the masses of central supermassive black holes and bulge mass or velocity dispersion suggest that such galaxies are likely to host black holes in their centres. The aim is to look for X-ray signs of activity in these gas-rich environments.
Methods.
We identified chandra ACIS-S images of the X-ray counterparts
of 9 sources from the optical sample. We isolated 10 individual X-ray sources
closest to the optical position and calculated their X-ray luminosity, LX,
and X-ray colours. Using Hα luminosities, we also calculated
star formation rates.
For four sources with a high number of net counts in the X-ray band, we
extracted X-ray spectra to which we fitted standard spectral models.
We modelled Fe Kα emission by Gaussians, and assessed the
significance of adding such a component to a fit by
means of a calibration of the standard F-test.
For the rest of the sources, we estimated values for
the intrinsic hydrogen column density, 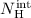 , and the power-law photon index, Γ, which can
reproduce the observed soft and hard X-ray colours.
, and the power-law photon index, Γ, which can
reproduce the observed soft and hard X-ray colours.
Results.
All spectral fits include a power law, a diffuse hot gas,
a Galactic absorption and
an intrinsic absorption component. For the nuclear sources of NGC 2782 and
NGC 3310, a Fe Kα emission-line component is included with
high significance. At the same time the power-law
component is flat (index 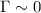 and 1.3).
Both sources have high star-formation rates, with the rate
for NGC 2782 being the highest in our sample.
and 1.3).
Both sources have high star-formation rates, with the rate
for NGC 2782 being the highest in our sample.
Conclusions.
The detection of Fe Kα emission coming from a central,
isolated source in NGC 2782 and NGC 3310, points towards
a hidden AGN in two out of nine relatively early-type, star-forming
spirals observed both with Palomar and Chandra. Larger samples need to
be explored, but this evidence suggests that the presence of
an AGN is likely in massive, disturbed starbursts. The
contribution of X-ray emission from these AGN is small: For the
central source, the
bolometric luminosity is a fraction of a few  10-5 of the
Eddington luminosity. The X-ray flux of the central source is between
10 and 20% of the total galactic flux in the
10-5 of the
Eddington luminosity. The X-ray flux of the central source is between
10 and 20% of the total galactic flux in the 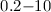 keV band.
keV band.
Key words: X-rays: galaxies / galaxies: starburst / galaxies: active / galaxies: individual: NGC 2782 / galaxies: individual: NGC 3310
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


