| Issue |
A&A
Volume 465, Number 1, April I 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 35 - 40 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20065920 | |
| Published online | 22 January 2007 | |
The soft X-ray cluster-AGN spatial cross-correlation function in the ROSAT-NEP survey
1
Max Planck Institute für Extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany e-mail: cappelluti@mpe.mpg.de
2
California Institute of Technology, Mail Code 130-33, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
3
Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089-0484, USA
4
Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan, 918 Dennison, 500 Church Street, Ann Arbor, 48109-1042, USA
5
Istituto di Radioastronomia INAF, via P. Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
6
Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai'i, 2680 Woodlawn Drive, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA
Received:
27
June
2006
Accepted:
16
November
2006
Context.X-ray surveys facilitate investigations of the environment of AGNs. Deep Chandra observations have revealed that the AGN source surface density rises near clusters of galaxies. The natural extension of this finding is the measurement of spatial clustering of AGNs around clusters and the investigation of relative biasing between active galactic nuclei and galaxies near clusters.
Aims.We aim to measure the correlation length of AGNs around clusters and the average clustering properties of a complete sample of AGNs in a dense environment.
Methods.We present the first measurement of the soft X-ray cluster-AGN
cross-correlation function in redshift space using the data of the
ROSAT-NEP survey. The survey covers 9  9 deg2 around
the North Ecliptic Pole where 442 X-ray sources were detected and
almost completely spectroscopically identified.
9 deg2 around
the North Ecliptic Pole where 442 X-ray sources were detected and
almost completely spectroscopically identified.
Results.We detected a >3σ significant clustering signal on scales
s ≤ 50  Mpc. We performed a classical
maximum-likelihood power-law fit to the data and obtained a correlation length s0 = 8.7
Mpc. We performed a classical
maximum-likelihood power-law fit to the data and obtained a correlation length s0 = 8.7
 Mpc and a slope γ = 1.7
Mpc and a slope γ = 1.7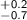 (1σ errors).
(1σ errors).
Conclusions.This is strong evidence that AGNs are good tracers of the large scale structure of the Universe. Our data were compared to the results obtained by cross-correlating X-ray clusters and galaxies. We observe, with a large uncertainty, a similar behaviour of AGN clustering around clusters similar to the clustering of galaxies around clusters.
Key words: galaxies: clusters: general / galaxies: active / X-rays: galaxies: clusters / cosmology: large-scale structure of Universe / cosmology: dark matter
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


