| Issue |
A&A
Volume 463, Number 2, February IV 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 635 - 640 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066572 | |
| Published online | 27 November 2006 | |
IRAS 08572+3915: constraining the aromatic versus aliphatic content of interstellar HACs *,**,***
1
Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, UMR-8617, Université Paris-Sud, bâtiment 121, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France e-mail: emmanuel.dartois@ias.u-psud.fr
2
Gemini Observatory, 670 North Aòhoku Place, Hilo, HI 96720, USA
3
Laboratoire de Photophysique Moléculaire, UPR 3361, Université Paris-Sud, bâtiment 210, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France
4
Service d'Aéronomie, UMR 7620, Route des Gatines, BP 3, 91371 Verrières Le Buisson, France
Received:
16
October
2006
Accepted:
22
November
2006
We analyze dust features present in the mid-infrared
(Spitzer) and recently published L-band (UKIRT) spectra of the infrared
galaxy IRAS 08572+3915. The line of sight toward the AGN nucleus crosses a
high column density of carbonaceous dust whose characteristic absorption
features appear clearly. They provide a real insight into the chemical
environment of the diffuse interstellar medium. Thanks to the moderate
redshift of IRAS 08572+3915, the wavelength of the aromatic CH stretching
mode is free of major telluric lines, and a strong observational
constraint of H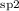 /H
/H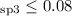 has been determined. This limit
clearly shows that the bonding of hydrogen atoms in interstellar
hydrogenated amorphous carbon is highly aliphatic. The presence of a broad
absorption feature centered at 6.2 μm, probably arising from
olefinic/aromatic structures, corresponds to the backbone of this
carbonaceous material, which is the major carbon-containing component of
the interstellar medium along this line of sight.
has been determined. This limit
clearly shows that the bonding of hydrogen atoms in interstellar
hydrogenated amorphous carbon is highly aliphatic. The presence of a broad
absorption feature centered at 6.2 μm, probably arising from
olefinic/aromatic structures, corresponds to the backbone of this
carbonaceous material, which is the major carbon-containing component of
the interstellar medium along this line of sight.
Key words: ISM: abundances / ISM: dust, extinction / galaxies: individual: IRAS 08572+3915 / galaxies: ISM
Based on observations made with the Spitzer Space Telescope (GO-3336 program), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology under NASA contract 1407.
Based on data obtained at the United Kingdom Infrared Telescope, which is operated by the Joint Astronomy Center on behalf of the UK Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council.
Part of this work has been financed by the french CNRS program "Physique et Chimie du Milieu Interstellaire" (PCMI-CNRS). TRG's esearch is supported by the Gemini Observatory, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., on behalf of the international Gemini partnership of Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America.
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


