| Issue |
A&A
Volume 463, Number 1, February III 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 69 - 78 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066566 | |
| Published online | 20 November 2006 | |
The HeII Lyman alpha forest and the thermal state of the IGM
Hamburger Sternwarte, Universität Hamburg, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany e-mail: [cfechner,dreimers]@hs.uni-hamburg.de
C. Fechner
Received:
13
October
2006
Accepted:
15
November
2006
Aims.Recent analyses of the intergalactic UV background by means of the  Lyα forest assume that
Lyα forest assume that  and
and 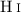 absorption features have the same line widths.
We omit this assumption to investigate possible effects of thermal line broadening on the inferred
absorption features have the same line widths.
We omit this assumption to investigate possible effects of thermal line broadening on the inferred  /
/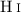 ratio η and to explore the potential of intergalactic
ratio η and to explore the potential of intergalactic  observations to constrain the thermal state of the intergalactic medium.
observations to constrain the thermal state of the intergalactic medium.
Methods.Deriving a simple relation between the column density and the temperature of an absorber based on the temperature-density relation  we develop a procedure to fit T0, γ, and η simultaneously by modeling the observed spectra with Doppler profiles.
In an alternative approach the temperature T of an absorber, the
we develop a procedure to fit T0, γ, and η simultaneously by modeling the observed spectra with Doppler profiles.
In an alternative approach the temperature T of an absorber, the  /
/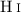 ratio η, and the redshift scale of η variations are estimated simultaneously by optimizing the Doppler parameters of
ratio η, and the redshift scale of η variations are estimated simultaneously by optimizing the Doppler parameters of  .
.
Results.Testing our procedure with artificial data shows that well-constrained results can be obtained only if the signal-to-noise ratio in the  forest is
forest is 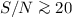 .
Additionally, ambiguities in the line profile decomposition may result in significant systematic errors.
Thus, it is impossible to give an estimate of the temperature-density relation with the
.
Additionally, ambiguities in the line profile decomposition may result in significant systematic errors.
Thus, it is impossible to give an estimate of the temperature-density relation with the  data available at present (
data available at present (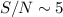 ).
However, we find that only 45% of the lines in our sample favor turbulent line widths while the remaining lines are probably affected by thermal broadening.
Furthermore, the inferred η values are on average about
).
However, we find that only 45% of the lines in our sample favor turbulent line widths while the remaining lines are probably affected by thermal broadening.
Furthermore, the inferred η values are on average about 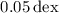 larger if a thermal component is taken into account, and their distribution is 46% narrower in comparison to a purely turbulent fit.
Therefore, variations of η on a 10% level may be related to the presence of thermal line broadening.
The apparent correlation between the strength of the
larger if a thermal component is taken into account, and their distribution is 46% narrower in comparison to a purely turbulent fit.
Therefore, variations of η on a 10% level may be related to the presence of thermal line broadening.
The apparent correlation between the strength of the 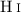 absorption and the η value, which has been found in former studies assuming turbulent line broadening, essentially disappears if thermal broadening is taken into account.
In the redshift range
absorption and the η value, which has been found in former studies assuming turbulent line broadening, essentially disappears if thermal broadening is taken into account.
In the redshift range 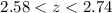 towards the quasars
HE 2347-4342 and HS 1700+6416 we obtain
towards the quasars
HE 2347-4342 and HS 1700+6416 we obtain 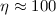 and slightly larger.
In the same redshift range the far-UV spectrum of HS 1700+6416 is best
and we estimate a mean value of
and slightly larger.
In the same redshift range the far-UV spectrum of HS 1700+6416 is best
and we estimate a mean value of 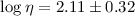 taking into account combined thermal and turbulent broadening.
taking into account combined thermal and turbulent broadening.
Key words: cosmology: observations / quasars: absorption lines / quasars: individual: HE 2347-4342 / quasars: individual: HS 1700+6416 / intergalactic medium
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


