| Issue |
A&A
Volume 461, Number 3, January III 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1103 - 1106 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066418 | |
| Published online | 24 October 2006 | |
Discovery of a new cataclysmic variable through optical variability and X-ray emission
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK e-mail: [mlp;christian]@astro.soton.ac.uk
Received:
19
September
2006
Accepted:
16
October
2006
Aims.We present discovery observations of the new cataclysmic variable star (CV) 1RXS J092737.4-191529, as well as spectra and photometry of SY Vol. The selection technique that turned up these two CVs is described; it should be efficient for finding dwarf novae with high outburst duty cycles.
Methods.Two very common observational features of CVs, namely optical variability and X-ray emission, are combined to select targets for follow-up observations. Long-slit spectra were taken to identify CVs in the sample.
Results.Two out of three objects selected in this way are CVs. One of these is the known dwarf nova SY Vol, while the second system, 1RXS J092737.4-191529, is a new discovery. We present medium resolution spectra, 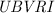 magnitudes, and high-speed photometry for both these CVs. Rapid flickering in the light curve of 1RXS J092737.4-191529 confirms the mass transferring binary nature of this object; it is probably a dwarf nova that was in quiescence during our observations.
magnitudes, and high-speed photometry for both these CVs. Rapid flickering in the light curve of 1RXS J092737.4-191529 confirms the mass transferring binary nature of this object; it is probably a dwarf nova that was in quiescence during our observations.
Key words: stars: dwarf novae / stars: novae, cataclysmic variables / stars: variables: general
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


