| Issue |
A&A
Volume 461, Number 3, January III 2007
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 923 - 929 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20066122 | |
| Published online | 16 October 2006 | |
Constraining the spectral age of very asymmetric CSOs
Evidence of the influence of the ambient medium
1
Dipartimento di Astronomia, Università di Bologna, via Ranzani 1, 40127 Bologna, Italy e-mail: orienti@ira.inaf.it
2
Istituto di Radioastronomia – INAF, via Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
Received:
27
July
2006
Accepted:
25
September
2006
Aims.We constrain the spectral ages for two very asymmetric Compact Symmetric Objects (CSO) from the B3-VLA-CSS sample, and we investigate the role of the ambient medium potentially able to influence the individual source evolution.
Methods. Multi-frequency VLBA observations have been carried out to study the distribution of the break frequency of the spectra across different regions of each source.
Results. From the analysis of synchrotron spectra and assuming an equipartition
magnetic field, we find radiative ages of about 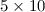 3
and
3
and 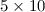 4 years for B0147+400 and B0840+424,
respectively.
The derived individual hot-spot advance speed is in the range between
0.03c and 0.3c, in agreement with kinematic studies carried out on
other CSOs. The very asymmetric morphology found in both sources
is likely related to an inhomogeneous ambient medium in which the
sources are growing, rather than to different intrinsic hot-spot
pressures on the two sides.
4 years for B0147+400 and B0840+424,
respectively.
The derived individual hot-spot advance speed is in the range between
0.03c and 0.3c, in agreement with kinematic studies carried out on
other CSOs. The very asymmetric morphology found in both sources
is likely related to an inhomogeneous ambient medium in which the
sources are growing, rather than to different intrinsic hot-spot
pressures on the two sides.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: evolution / radio continuum: galaxies / radiation mechanisms: non-thermal / galaxies: ISM
© ESO, 2007
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


