| Issue |
A&A
Volume 460, Number 1, December II 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 125 - 131 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054784 | |
| Published online | 15 September 2006 | |
Diagnostics of SS433 with the RXTE
1
Max-Planck-Institute für Astrophysik, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 1, 85740 Garching bei München, Germany
2
Space Research Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Profsoyuznaya 84/32, 117997 Moscow, Russia e-mail: kate@hea.iki.rssi.ru
3
Special Astrophysical Observatory, Nizhnij Arkhyz, Karachaevo-Cherkesiya 369167, Russia
4
Sternberg Astronomical Institute, 119992 Moscow, Russia
Received:
28
December
2005
Accepted:
24
August
2006
We present our analysis of the extensive monitoring of SS433
by the RXTE observatory collected over the period 1996–2005. The
difference between energy spectra taken at different precessional
and orbital phases shows the presence of strong photoabsorption
(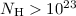 cm-2) near the optical star,
probably due to its powerful, dense wind.
Therefore the size of the secondary deduced from analysis of
X-ray orbital eclipses might be significantly larger than its Roche
lobe size, which must be taken into account when
evaluating the mass ratio from analysis of X-ray eclipses.
Assuming that a precessing accretion disk
is geometrically thick, we recover the temperature
profile in the X-ray emitting jet that best fits the observed
precessional variations in the X-ray emission temperature.
The hottest visible part of the X-ray jet is located at
a distance of
cm-2) near the optical star,
probably due to its powerful, dense wind.
Therefore the size of the secondary deduced from analysis of
X-ray orbital eclipses might be significantly larger than its Roche
lobe size, which must be taken into account when
evaluating the mass ratio from analysis of X-ray eclipses.
Assuming that a precessing accretion disk
is geometrically thick, we recover the temperature
profile in the X-ray emitting jet that best fits the observed
precessional variations in the X-ray emission temperature.
The hottest visible part of the X-ray jet is located at
a distance of 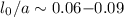 , or ~
, or ~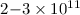 cm from the
central compact object, and has a temperature of about
cm from the
central compact object, and has a temperature of about 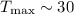 keV.
We discovered appreciable orbital X-ray
eclipses at the “crossover” precessional phases (jets are in the
plane of the sky, disk is edge-on), which under model assumptions
put a lower limit
on the size of the optical component
keV.
We discovered appreciable orbital X-ray
eclipses at the “crossover” precessional phases (jets are in the
plane of the sky, disk is edge-on), which under model assumptions
put a lower limit
on the size of the optical component 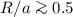 and an upper
limit on a mass ratio of binary companions
and an upper
limit on a mass ratio of binary companions 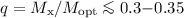 , if the X-ray opaque size of the star is not
larger than
, if the X-ray opaque size of the star is not
larger than 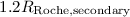 .
.
Key words: accretion, accretion disks / black hole physics / binaries: eclipsing / X-rays: binaries / radiation mechanisms: general
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


