| Issue |
A&A
Volume 459, Number 1, November III 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 291 - 296 | |
| Section | Atomic, molecular, and nuclear data | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054660 | |
| Published online | 12 September 2006 | |
Determination of the recombination rate coefficients for Na-like Si IV forming Mg-like Si III
1
Department of Atomic Physics, Stockholm University, 106 91 Stockholm, Sweden e-mail: istvan.orban@physto.se
2
Department of Engineering, Physics and Mathematics, Mid Sweden University, 851 70 Sundsvall, Sweden
3
Department of Physics, Marmara University, 81040 Istanbul, Turkey
4
Manne Siegbahn Laboratory, Stockholm University, 104 05 Stockholm, Sweden
Received:
7
December
2005
Accepted:
9
June
2006
Aims.Absolute, total recombination rate coefficients for 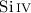 were determined using the CRYRING heavy-ion storage ring. Calculated rate coefficients were used to estimate recombination into states that could not be detected in the experiment because of field ionization. Total, as well as separate, radiative and dielectronic plasma recombination rate coefficients were determined.
were determined using the CRYRING heavy-ion storage ring. Calculated rate coefficients were used to estimate recombination into states that could not be detected in the experiment because of field ionization. Total, as well as separate, radiative and dielectronic plasma recombination rate coefficients were determined.
Methods.Stored ions were merged with an expanded electron beam in the electron cooler section of the storage ring. Recombined ions were separated from the stored ion beam in the first dipole magnet after the electron cooler and were detected with unity efficiency. The absolute radiative and dielectronic
recombination rate coefficients were obtained over a center-of-mass energy range of 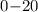 eV, covering
eV, covering 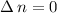 core excitations
up to the
core excitations
up to the 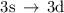 series limit. The results of an intermediate
coupling autostructure calculation were compared with the experiment.
The theoretical results were also used to estimate the contribution to dielectronic recombination by high Rydberg states, which were not detected because of field ionization. The spectra were
convoluted with Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distributions in the
series limit. The results of an intermediate
coupling autostructure calculation were compared with the experiment.
The theoretical results were also used to estimate the contribution to dielectronic recombination by high Rydberg states, which were not detected because of field ionization. The spectra were
convoluted with Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distributions in the 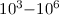 K
temperature range.
K
temperature range.
Results.The resulting plasma recombination rate
coefficients are presented and compared with theoretical results
frequently used for plasma modeling. In the 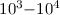 K range, a
significant underestimation of the calculated dielectronic recombination plasma rate coefficients was
observed. Above
K range, a
significant underestimation of the calculated dielectronic recombination plasma rate coefficients was
observed. Above 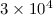 K, the agreement between our dielectronic recombination plasma rate
coefficients and two of the previously
published rate coefficients is better than
K, the agreement between our dielectronic recombination plasma rate
coefficients and two of the previously
published rate coefficients is better than 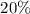 .
.
Conclusions.The observed differences between the experimental and calculated recombination rate coefficients at low temperatures reflect the need for benchmarking experiments. Our experimentally-derived rate coefficients can guide the development of better theoretical models and lead to more accurately-calculated rate coefficients.
Key words: atomic data / atomic processes / plasmas
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


