| Issue |
A&A
Volume 457, Number 3, October III 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 779 - 785 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054743 | |
| Published online | 12 September 2006 | |
The multi-phase gaseous halos of star-forming late-type galaxies
II. Statistical analysis of key parameters
1
Astronomisches Institut, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, 44780 Bochum, Germany e-mail: [tullmann;dettmar]@astro.rub.de
2
Institut für Astronomie, Türkenschanzstrasse 17, 1180 Wien, Austria e-mail: breitschwerdt@astro.univie.ac.at
3
Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA e-mail: jrossa@stsci.edu
4
Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse, 85748 Garching, Germany e-mail: wnp@mpe.mpg.de
Received:
21
December
2005
Accepted:
21
April
2006
Context.In a previous paper (Paper I) we showed that multi-phase gaseous halos of late-type spiral galaxies, detected in the radio continuum, in Hα, and in X-rays, are remarkably well correlated regarding their morphology and spatial extent.
Aims.In this work we present new results from a statistical analysis to specify and quantify these phenomenological relations in more detail.
Methods.This is accomplished by investigating soft X-ray (0.3-2.0 keV) luminosities, FIR, radio continuum (1.4 GHz), Hα, B-band, and UV (1550-1650 Å) luminosities for a sample of 23 edge-on late-type spiral galaxies. Typical star formation indicators, such as star formation rates (SFRs), are determined and a statistical multi-parameter/frequency correlation analysis is carried out.
Results.We find strong linear correlations, covering at least two orders of magnitude, between star formation indicators and integrated (disk+halo) luminosities in all covered wavebands. In addition to the well-established 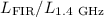 relation, we show new and highly significant linear dependencies between integrated soft X-ray luminosities and FIR, radio continuum, Hα, B-band, and UV luminosities. Moreover, integrated soft X-ray luminosities correlate well with SFRs and the energy input into the ISM by SNe. The same holds if these quantities are plotted against soft halo X-ray luminosities. Only a weak correlation exists between the dust mass of a galaxy and the corresponding X-ray luminosity. Among soft X-ray luminosities, baryonic, and
relation, we show new and highly significant linear dependencies between integrated soft X-ray luminosities and FIR, radio continuum, Hα, B-band, and UV luminosities. Moreover, integrated soft X-ray luminosities correlate well with SFRs and the energy input into the ISM by SNe. The same holds if these quantities are plotted against soft halo X-ray luminosities. Only a weak correlation exists between the dust mass of a galaxy and the corresponding X-ray luminosity. Among soft X-ray luminosities, baryonic, and 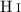 gas masses, no significant correlations are found. There seems to exist a critical input energy by SNe into the ISM or a SFR threshold for multi-phase halos to appear. It is still not clear whether this threshold is a physical one or represents an instrument-dependent sensitivity limit.
gas masses, no significant correlations are found. There seems to exist a critical input energy by SNe into the ISM or a SFR threshold for multi-phase halos to appear. It is still not clear whether this threshold is a physical one or represents an instrument-dependent sensitivity limit.
Conclusions.These findings strongly support our previous results that multi-phase gaseous galaxy halos in late-type spiral galaxies are created and maintained by outflowing gas produced in star formation processes in the disk plane. They conflict with the concept of halos being mainly due to infalling gas from the intergalactic medium.
Key words: galaxies: formation / galaxies: halos / galaxies: ISM / galaxies: spiral / galaxies: starburst / X-rays: galaxies / X-rays: ISM
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


