| Issue |
A&A
Volume 454, Number 2, August I 2006
APEX Special Booklet
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L33 - L36 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20065341 | |
| Published online | 11 July 2006 | |
Letter to the Editor
First observations with CONDOR, a 1.5 THz heterodyne receiver
1
I. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Str. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany e-mail: lastname@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany e-mail: lastname@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
3
European Southern Observatory, Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Casilla 19001, Santiago, Chile e-mail: initial.lastname@eso.org
Received:
31
March
2006
Accepted:
31
May
2006
Context.The THz atmospheric “windows”, centered at roughly 1.3 and 1.5 THz, contain numerous spectral lines of astronomical importance, including three high-J CO lines, the [N II] line at 205 μm, and the ground transition of para-H2D+. The CO lines are tracers of hot (several 100 K), dense gas; [N II] is a cooling line of diffuse, ionized gas; the H2D+ line is a non-depleting tracer of cold (~20 K), dense gas.
Aims.As the THz lines benefit the study of diverse phenomena (from high-mass star-forming regions to the WIM to cold prestellar cores), we have built the CO N+ Deuterium Observations Receiver (CONDOR) to further explore the THz windows by ground-based observations.
Methods.CONDOR was designed to be used at the Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment (APEX) and Stratospheric Observatory For Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA). CONDOR was installed at the APEX telescope and test observations were made to characterize the instrument.
Results.The combination of CONDOR on APEX successfully detected THz radiation
from astronomical sources. CONDOR operated with typical 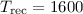 K
and spectral Allan variance times of ~30 s. CONDOR's “first light”
observations of CO 13-12 emission from the hot core Orion FIR 4 (= OMC1 South)
revealed a narrow line with
K
and spectral Allan variance times of ~30 s. CONDOR's “first light”
observations of CO 13-12 emission from the hot core Orion FIR 4 (= OMC1 South)
revealed a narrow line with 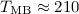 K and
K and
 km s-1. A search for [N II] emission from the
ionization front of the Orion Bar resulted in a non-detection.
km s-1. A search for [N II] emission from the
ionization front of the Orion Bar resulted in a non-detection.
Conclusions.The successful deployment of CONDOR at APEX demonstrates the potential for making observations at THz frequencies from ground-based facilities.
Key words: instrumentation: detectors / methods: observational / submillimeter / stars: formation / HII regions / Orion FIR4
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


