| Issue |
A&A
Volume 453, Number 2, July II 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 525 - 533 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054203 | |
| Published online | 16 June 2006 | |
The correlation of narrow line emission and X-ray luminosity in active galactic nuclei
1
School of Physics and Astronomy and the Wise Observatory, The Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel e-mail: netzer@wise.tau.ac.il
2
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany
3
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, 85748 Garching bei Muenchen, Germany
Accepted: 14 September 2005
Aims.We combine emission line and X-ray luminosities for 45 sources
from the Chandra Deep Field South (CDF-S), and seven
HELLAS sources, to obtain a new sample of 52 X-ray selected
type-II active galactic nuclei (AGNs). Eighteen of our sources are very luminous with a typical,
absorption-corrected 2–10 keV luminosity of 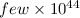 erg s-1 (type-II QSOs).
erg s-1 (type-II QSOs).
Methods. We compare the emission line properties of the new sources with emission line and X-ray luminosities of known low redshift, mostly lower luminosity AGNs by using a composite spectrum.
Results.
We find that ![$L_{{\rm [OIII]}}$](/articles/aa/abs/2006/26/aa4203-05/aa4203-05_tex_eq2.png) /
/ and
and ![$L_{{\rm [OII]}}$](/articles/aa/abs/2006/26/aa4203-05/aa4203-05_tex_eq4.png) /
/ decrease with L(2–10 keV) such that
decrease with L(2–10 keV) such that
![$L_{{\rm [OIII]}}$](/articles/aa/abs/2006/26/aa4203-05/aa4203-05_tex_eq2.png) /
/
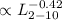 .
The trend was already evident, yet neglected in past low redshift samples.
This lead to erroneous calibration of the line-to-X-ray luminosity in earlier AGN samples.
The analysis of several type-I samples shows the same trend with a similar slope
but a median
.
The trend was already evident, yet neglected in past low redshift samples.
This lead to erroneous calibration of the line-to-X-ray luminosity in earlier AGN samples.
The analysis of several type-I samples shows the same trend with a similar slope
but a median ![$L_{{\rm [OIII]}}$](/articles/aa/abs/2006/26/aa4203-05/aa4203-05_tex_eq2.png) /
/ which is larger by a factor of about two compared with optically selected
type-II samples. We interpret this shift as due to additional reddening
in type-II sources and comment in general on the very large extinction in many type-II objects
and the significantly smaller average reddening of the SDSS type-II AGNs.
The decrease of
which is larger by a factor of about two compared with optically selected
type-II samples. We interpret this shift as due to additional reddening
in type-II sources and comment in general on the very large extinction in many type-II objects
and the significantly smaller average reddening of the SDSS type-II AGNs.
The decrease of ![$L_{{\rm [OIII]}}$](/articles/aa/abs/2006/26/aa4203-05/aa4203-05_tex_eq2.png) /
/ with L(2–10 keV) is
large enough to suggest that a significant fraction of high luminosity
high redshift type-II AGNs have very weak emission lines that may have
escaped detection in large samples. A related decrease of EW([O iii]
with L(2–10 keV) is
large enough to suggest that a significant fraction of high luminosity
high redshift type-II AGNs have very weak emission lines that may have
escaped detection in large samples. A related decrease of EW([O iii] 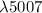 ) with optical continuum luminosity
is demonstrated by an analysis of 12 000 type-I SDSS AGNs.
The new correlations found here are important for deriving accurate luminosity functions
for AGNs and their neglect may explain past discrepancies between emission line and
X-ray samples.
) with optical continuum luminosity
is demonstrated by an analysis of 12 000 type-I SDSS AGNs.
The new correlations found here are important for deriving accurate luminosity functions
for AGNs and their neglect may explain past discrepancies between emission line and
X-ray samples.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: Seyfert / quasars: emission lines / X-rays: galaxies
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


