| Issue |
A&A
Volume 452, Number 1, June II 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 25 - 35 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20054283 | |
| Published online | 17 May 2006 | |
Time delay of SBS 0909+532
1
Departamento de Física Moderna, Universidad de Cantabria, Avda. de Los Castros s/n, 39005 Santander, Spain e-mail: aurora.ullan@postgrado.unican.es; goicol@unican.es
2
Institute of Astronomy of Kharkov National University, Sumskaya 35, 61022 Kharkov, Ukraine e-mail: zheleznyak@astron.kharkov.ua
3
Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Universitetski Pr. 13, 119992 Moscow, Russia e-mail: koptelova@xray.sai.msu.ru; bruevich@sai.msu.ru
4
Ulug Beg Astronomical Institute of Uzbek Academy of Science, Astronomicheskaya. Str. 33, 700052 Tashkent, Republic of Uzbekistan e-mail: talat77@rambler.ru; boa@astrin.uzsci.net
Received:
30
September
2005
Accepted:
12
January
2006
Aims.The time delays between the components of a lensed quasar are basic tools for analysing the expansion of the Universe and the structure of the main lens galaxy halo. In this paper, we focus on the variability and time delay of the double system SBS 0909+532A,B as well as the time behaviour of the field stars.
Methods.We use VR optical observations of SBS 0909+532A, B and the field stars in 2003. The frames
were taken at Calar Alto, Maidanak, and Wise observatories, and the VR light curves of the
field stars and quasar components were derived from aperture and point-spread function fitting
methods. We measured the R-band time delay of the system from the 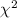 and dispersion
techniques and 1000 synthetic light curves based on the observed records.
and dispersion
techniques and 1000 synthetic light curves based on the observed records.
Results.One nearby field star (SBS 0909+532c) was found to be variable, and the other two nearby field
stars are non-variable sources. With respect to the quasar components, the R-band records seem
more reliable and are more densely populated than the V-band ones. The observed R-band
fluctuations permit a pre-conditioned measurement of the time delay. From the 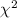 minimization, if we assume that the quasar emission is observed first in B and afterwards in A (in
agreement with basic observations of the system and the corresponding predictions), we obtain
minimization, if we assume that the quasar emission is observed first in B and afterwards in A (in
agreement with basic observations of the system and the corresponding predictions), we obtain
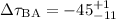 days (95% confidence interval). The dispersion technique
leads to a similar delay range. A by-product of the analysis is the determination of a totally
corrected flux ratio in the R band (corrected by the time delay and the contamination due to the
galaxy light). Our 95% measurement
days (95% confidence interval). The dispersion technique
leads to a similar delay range. A by-product of the analysis is the determination of a totally
corrected flux ratio in the R band (corrected by the time delay and the contamination due to the
galaxy light). Our 95% measurement 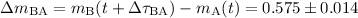 mag is in excellent agreement with previous results from contaminated fluxes at
the same time of observation.
mag is in excellent agreement with previous results from contaminated fluxes at
the same time of observation.
Key words: gravitational lensing / galaxies: quasars: general / galaxies: quasars: individual: SBS 0909+532 / stars: variables: general
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


