| Issue |
A&A
Volume 451, Number 3, June I 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 917 - 924 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053845 | |
| Published online | 04 May 2006 | |
[CII] 158 μm emission and metallicity in photon dominated regions
1
I. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Str. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany e-mail: roellig@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
SRON National Institute for Space Research, PO Box 800, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands
3
School of Physics and Astronomy, Tel Aviv University, Ramat Aviv 69978, Israel
Received:
18
July
2005
Accepted:
14
November
2005
We study the effects of a metallicity variation on
the thermal balance and [CII] fine-structure line
strengths in
interstellar photon dominated regions (PDRs).
We find that a reduction in the dust-to-gas ratio and
the abundance of heavy elements in the gas phase
changes the heat balance of the gas in PDRs.
The surface temperature of PDRs decreases as
the metallicity decreases except for high density
(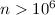 cm-3) clouds exposed to weak (
cm-3) clouds exposed to weak (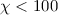 ) FUV fields where
vibrational
H2-deexcitation heating dominates over photoelectric heating of the gas.
We incorporate the metallicity dependence in our KOSMA-τ PDR model
to study the metallicity dependence of [CII]/CO line ratios
in low metallicity galaxies. We find that the main trend in the variation
of the observed CII/CO ratio with metallicity is well reproduced
by a single spherical clump, and does not necessarily require
an ensemble of clumps as in the semi-analytical model presented
by Bolatto et al. (1999).
) FUV fields where
vibrational
H2-deexcitation heating dominates over photoelectric heating of the gas.
We incorporate the metallicity dependence in our KOSMA-τ PDR model
to study the metallicity dependence of [CII]/CO line ratios
in low metallicity galaxies. We find that the main trend in the variation
of the observed CII/CO ratio with metallicity is well reproduced
by a single spherical clump, and does not necessarily require
an ensemble of clumps as in the semi-analytical model presented
by Bolatto et al. (1999).
Key words: ISM: abundances / ISM: structure / ISM: clouds / ISM: general / galaxies: ISM / galaxies: abundances
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


