| Issue |
A&A
Volume 451, Number 3, June I 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 999 - 1008 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053841 | |
| Published online | 04 May 2006 | |
A comprehensive study of the SX Phoenicis star BL Camelopardalis
1
Association AstroQueyras, Le bois de Bardon, Taponnat, 16110 La Rochefoucauld, France e-mail: stephane.fauvaud@wanadoo.fr
2
Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, CSIC, PO Box 3004, 18080 Granada, Spain e-mail: eloy@iaa.es
3
National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100012, PR China
4
Department of Physics, Astronomy, and Materials Science, Missouri State University, 901 S. National, Springfield, MO 65897, USA
5
Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur, BP 4229, 06304 Nice Cedex 4, France
6
Institut de Ciéncies de l'Espai, CSIC, Facultat de Ciéncies, Campus UAB, Torre C5-parell, 2$^a$ planta, 08193 Bellaterra, Spain
7
Institut d'Estudis Espacials de Catalunya (IEEC), C/Gran Capitá 2-4, 08034 Barcelona, Spain
8
Norwegian Astronomical Society, Engeshaugen 15, 8616 Mo i Rana, Norway
9
Sulphur Flats Observatory, 449 Sulphur Creek Road, Jemez Springs, NM 87025, USA
10
Club d'Astronomie Lyon Ampère, 37 rue Paul Cazeneuve, 69008 Lyon, France
11
American Association of Variable Star Observers, 25 Birch Street, Cambridge, MA 02138, USA
Received:
18
July
2005
Accepted:
5
January
2006
Context.BL Cam is an extreme field multiperiodic short-period low-metallicity high-amplitude SX Phe-type variable where its probably complex pulsational content is subject of controversies.
Aims.A comprehensive study has been carried out to investigate the nature and pulsational properties of this object.
Methods.The analysis is based on new photometric data collected during the last few years at different sites, as well as on all available previously published data. Frequency analyses have been performed on a number of reliable data sets to analyse the pulsational content. In addition, the classical O-C method was used to study the behaviour of the main period.
Results.Our frequency analysis confirms some aspects on the multiperiodicity
of BL Cam, previously found by other authors, showing a number of
secondary modes close to the main frequency 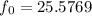 cd-1.
The secondary modes present eventual amplitude variations. However,
the main frequency exhibits no significant changes in its
amplitude and seems to correspond to the fundamental mode of radial
pulsation. Abrupt changes
sometimes observed in the light curves could be due to spurious activity on or
close to the star's photosphere.
We confirm the existence of a secondary
frequency at 31.6 or 32.6 cd-1, with variable amplitude, and with the
possibility of both frequencies being intrinsic to the star.
More than one hundred of new times of light maxima have been determined in
the present work. These together with those available in the literature allow
us a more discriminating analysis of the O–C diagram. This shows that the
observed variations of the main period can be described by two terms:
(i) a secular increase
of the main period at a rate of
cd-1.
The secondary modes present eventual amplitude variations. However,
the main frequency exhibits no significant changes in its
amplitude and seems to correspond to the fundamental mode of radial
pulsation. Abrupt changes
sometimes observed in the light curves could be due to spurious activity on or
close to the star's photosphere.
We confirm the existence of a secondary
frequency at 31.6 or 32.6 cd-1, with variable amplitude, and with the
possibility of both frequencies being intrinsic to the star.
More than one hundred of new times of light maxima have been determined in
the present work. These together with those available in the literature allow
us a more discriminating analysis of the O–C diagram. This shows that the
observed variations of the main period can be described by two terms:
(i) a secular increase
of the main period at a rate of 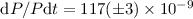 yr-1;
and (ii) a perturbation from a companion star in a rather eccentric orbit
with a period of 10.5(±0.2) yr causing a light time semi-amplitude of
148(±12) s.
yr-1;
and (ii) a perturbation from a companion star in a rather eccentric orbit
with a period of 10.5(±0.2) yr causing a light time semi-amplitude of
148(±12) s.
Key words: stars: variables: delta Sct / stars: individual: BL Cam / stars: oscillations / techniques: photometric
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


