| Issue |
A&A
Volume 447, Number 2, February IV 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 761 - 768 | |
| Section | Atomic, molecular, and nuclear data | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042511 | |
| Published online | 07 February 2006 | |
Benchmarking atomic data for astrophysics: 
University College London, MSSL, Holmbury St. Mary Dorking Surrey RH5 6NT, UK e-mail: gdz@mssl.ucl.ac.uk
Received:
9
December
2004
Accepted:
11
October
2005
Fe XXIV produces strong L-shell
(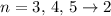 ) spectral lines in the X-rays.
These lines have been observed in solar flares,
in laboratory spectra, and in a variety of
astrophysical sources with e.g. the Chandra and XMM-Newton
satellites.
In this paper atomic data for Fe XXIV L-shell
emission are benchmarked against experimental data.
The work focuses on reviewing and assessing
previous line identifications on a quantitative basis,
paying particular attention to the most
important lines for laboratory
and astrophysical applications.
Previous identifications are confirmed,
but many lines turn out to be significantly blended.
The agreement between theoretical and observed data
in terms of wavelengths, line intensities and level lifetimes
is good, within the experimental uncertainties.
Fe XXIV L-shell lines can be used to measure electron
densities in laboratory plasmas and
temperatures for a wide range of astrophysical sources.
) spectral lines in the X-rays.
These lines have been observed in solar flares,
in laboratory spectra, and in a variety of
astrophysical sources with e.g. the Chandra and XMM-Newton
satellites.
In this paper atomic data for Fe XXIV L-shell
emission are benchmarked against experimental data.
The work focuses on reviewing and assessing
previous line identifications on a quantitative basis,
paying particular attention to the most
important lines for laboratory
and astrophysical applications.
Previous identifications are confirmed,
but many lines turn out to be significantly blended.
The agreement between theoretical and observed data
in terms of wavelengths, line intensities and level lifetimes
is good, within the experimental uncertainties.
Fe XXIV L-shell lines can be used to measure electron
densities in laboratory plasmas and
temperatures for a wide range of astrophysical sources.
Key words: atomic data / line: identification / Sun: flares / techniques: spectroscopic
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


