| Issue |
A&A
Volume 446, Number 3, February II 2006
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 897 - 904 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053892 | |
| Published online | 20 January 2006 | |
On the generation of asymmetric warps in disk galaxies
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India e-mail: [kanak;cjjog]@physics.iisc.ernet.in
Received:
23
July
2005
Accepted:
30
September
2005
Context.The warps in many spiral galaxies are now known to be asymmetric. Recent sensitive observations have revealed that asymmetry of warps may be the norm rather than exception. However there exists no generic mechanism to generate these asymmetries in warps.
Aims.To provide an explanation for the generation of asymmetric warps in disk galaxies
Methods.We have derived the dispersion relation in a compact form for the S-shaped warps (described by the 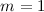 mode) and the bowl-shaped distribution (described by the
mode) and the bowl-shaped distribution (described by the 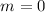 mode) in a galactic disk embedded in a dark matter halo. We then performed the numerical modal analysis and used the linear and time-dependent superposition principle to generate asymmetric warps in the disk.
mode) in a galactic disk embedded in a dark matter halo. We then performed the numerical modal analysis and used the linear and time-dependent superposition principle to generate asymmetric warps in the disk.
Results.On doing the modal analysis we find the frequency of the 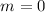 mode is much larger than that of the
mode is much larger than that of the 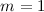 mode. The linear and time-dependent superposition of these modes with their unmodulated amplitudes (that is, the coefficients of superposition being unity) results in an asymmetry in warps of ~20–40 %, whereas a smaller coefficient for the
mode. The linear and time-dependent superposition of these modes with their unmodulated amplitudes (that is, the coefficients of superposition being unity) results in an asymmetry in warps of ~20–40 %, whereas a smaller coefficient for the 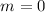 mode results in a smaller asymmetry. The resulting values agree well with the recent observations. We study the dependence of the asymmetry index on the dark matter halo parameters. This approach can also naturally produce U-shaped warps and L-shaped warps.
mode results in a smaller asymmetry. The resulting values agree well with the recent observations. We study the dependence of the asymmetry index on the dark matter halo parameters. This approach can also naturally produce U-shaped warps and L-shaped warps.
Conclusions.We show that a rich variety of possible asymmetries in the z-distribution of the spiral galaxies can naturally arise due to a dynamical wave interference between the first two bending modes (i.e. 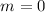 and
and 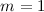 ) in the disk. This is a simple but general method for generating asymmetric warps that is independent of how the individual modes arise in the disk.
) in the disk. This is a simple but general method for generating asymmetric warps that is independent of how the individual modes arise in the disk.
© ESO, 2006
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


