| Issue |
A&A
Volume 442, Number 2, November I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 479 - 493 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041731 | |
| Published online | 07 October 2005 | |
Molecular gas in NUclei of GAlaxies (NUGA)
III. The warped LINER NGC 3718
1
Universität zu Köln, I.Physikalisches Institut, Zülpicher Str. 77, 50937 Köln, Germany e-mail: [krips;eckart]@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
Institut de Radio-Astronomie Millimétrique (IRAM), 300 rue de la Piscine, 38406 St. Martin-d'Hères, France e-mail: neri@iram.fr
3
ESO, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, 85748 Garching, Germany; e-mail: jpott@eso.org
4
Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (CSIC), C/ Camino Bajo de Huétor 24, Apartado 3004, 18080 Granada, Spain e-mail: stephane@iaa.es
5
Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Av. de l'Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France; e-mail: francoise.combes@obspm.fr
6
Observatorio Astronómico Nacional (OAN)-Observatorio de Madrid, Alfonso XII 3, 28014 Madrid, Spain e-mail: burillo@oan.es
7
Istituto di Radioastronomia/CNR, Sez. Firenze, Largo Enrico Fermi 5, 50125 Firenze, Italy e-mail: hunt@arcetri.astro.it
8
Jansky Fellow, National Radio Astronomy Observatory Department of Astronomy, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742-2421, USA; e-mail: ajb@astro.umd.edu
9
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, Postfach 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany; e-mail: linda@mpe.mpg.de
10
Astronomisches Institut, Universität Basel, Venusstr. 7, 4102 Binningen, Switzerland; e-mail: ppe@astro.unibas.ch
11
Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie, Königstuhl 17, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany; e-mail: schinner@mpia-hd.mpg.de
12
Max Planck Institut für Radioastronomie, Auf dem Hügel 69, 53121 Bonn, Germany e-mail: fboone@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de
Received:
26
July
2004
We present the first interferometric observations of
CO(1–0) and CO(2–1) line emission from the warped LINER
NGC 3718, obtained with the IRAM Plateau de Bure
Interferometer (PdBI). This L1.9 galaxy has a prominent dust lane
and on kiloparsec scales, a strongly warped atomic and molecular
gas disk. The molecular gas is closely associated with the dust
lane across the nucleus and its kinematic center is consistent with
the millimeter continuum AGN. A comparison of our interferometric
mosaic data, which fully cover the ~  warped disk,
with a previously obtained IRAM 30 m single dish CO(1–0) map
shows that the molecular gas distribution in the disk is heavily
resolved by the PdBI map. On the nucleus the interferometric maps
alone contain less than one half of the single dish line
flux, and the overall mosaic accounts for about a tenth of the
total molecular gas mass of
~
warped disk,
with a previously obtained IRAM 30 m single dish CO(1–0) map
shows that the molecular gas distribution in the disk is heavily
resolved by the PdBI map. On the nucleus the interferometric maps
alone contain less than one half of the single dish line
flux, and the overall mosaic accounts for about a tenth of the
total molecular gas mass of
~ 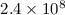
 .
After applying a short-spacing correction with the IRAM 30 m data to
recover the missing extended flux, we find in total six main source
components within the dust lane: one associated with the nucleus,
four symmetrically positioned on either side at galactocentric
distances of about 1.3 kpc and 4.0 kpc from the center, and a sixth
on the western side at ~
.
After applying a short-spacing correction with the IRAM 30 m data to
recover the missing extended flux, we find in total six main source
components within the dust lane: one associated with the nucleus,
four symmetrically positioned on either side at galactocentric
distances of about 1.3 kpc and 4.0 kpc from the center, and a sixth
on the western side at ~  with only a very weak
eastern counterpart. In the framework of a kinematic model using
tilted rings, we interpret the five symmetric source components as
locations of strong orbital crowding. We further find indications
that the warp appears not only on kpc scales, but continues down to
~
with only a very weak
eastern counterpart. In the framework of a kinematic model using
tilted rings, we interpret the five symmetric source components as
locations of strong orbital crowding. We further find indications
that the warp appears not only on kpc scales, but continues down to
~ 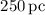 . Besides the sixth feature on the western
side, the lower flux (a factor of ~2) of the eastern
components compared to the western ones indicates an intrinsic
large scale asymmetry in NGC 3718 that cannot be explained by the
warp. Indications for a small scale asymmetry are also seen in the
central 600 pc. These asymmetries might be evidence for a tidal
interaction with a companion galaxy (large scales) and gas
accretion onto the nucleus (small scales). Our study of
NGC 3718 is part of the NUclei of GAlaxies (NUGA) project that aims
at investigating the different processes of gas accretion onto
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN).
. Besides the sixth feature on the western
side, the lower flux (a factor of ~2) of the eastern
components compared to the western ones indicates an intrinsic
large scale asymmetry in NGC 3718 that cannot be explained by the
warp. Indications for a small scale asymmetry are also seen in the
central 600 pc. These asymmetries might be evidence for a tidal
interaction with a companion galaxy (large scales) and gas
accretion onto the nucleus (small scales). Our study of
NGC 3718 is part of the NUclei of GAlaxies (NUGA) project that aims
at investigating the different processes of gas accretion onto
Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN).
Key words: galaxies: individual: NGC 3718 / galaxies: active / Galaxy: kinematics and dynamics
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


