| Issue |
A&A
Volume 441, Number 3, October III 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 961 - 973 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20053358 | |
| Published online | 23 September 2005 | |
Photon dominated regions in the spiral arms of M 83 and M 51
1
KOSMA, I. Physikalisches Institut, Universität zu Köln, Zülpicher Straße 77, 50937 Köln, Germany e-mail: kramer@ph1.uni-koeln.de
2
Radioastronomie Millimétrique: UMR 8540 du CNRS, Laboratoire de Physique de l'ENS, 24 rue Lhomond, 75231 Paris Cedex 05, France
3
Centro Astronomico de Yebes, IGN, 19080 Guadalajara, Spain
4
Sterrewacht Leiden, PO Box 9513, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands
5
Joint Astronomy Centre, 660 N. A'ohoku Place, 96720 Hilo, HI, USA
Received:
3
May
2005
Accepted:
2
June
2005
We present [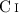 ] 3P1–3P0 spectra at four
spiral arm positions and the nuclei of the nearby galaxies M 83
and M 51 obtained at the JCMT. The spiral arm positions lie at
galacto-centric distances of between 2 kpc and 6 kpc. This data
is complemented with maps of CO 1–0, 2–1, and 3–2, and ISO/LWS
far-infrared data of [
] 3P1–3P0 spectra at four
spiral arm positions and the nuclei of the nearby galaxies M 83
and M 51 obtained at the JCMT. The spiral arm positions lie at
galacto-centric distances of between 2 kpc and 6 kpc. This data
is complemented with maps of CO 1–0, 2–1, and 3–2, and ISO/LWS
far-infrared data of [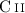 ] (158 μm), [
] (158 μm), [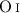 ] (63 μm), and
[
] (63 μm), and
[ ] (122 μm) allowing for the investigation of a complete
set of all major gas cooling lines. From the intensity of the
[
] (122 μm) allowing for the investigation of a complete
set of all major gas cooling lines. From the intensity of the
[ ] line, we estimate that between 15% and 30% of the
observed [
] line, we estimate that between 15% and 30% of the
observed [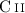 ] emission originates from the dense ionized phase
of the ISM. The analysis indicates that emission from the diffuse
ionized medium is negligible. In combination with the FIR dust
continuum, we find gas heating efficiencies below ~
] emission originates from the dense ionized phase
of the ISM. The analysis indicates that emission from the diffuse
ionized medium is negligible. In combination with the FIR dust
continuum, we find gas heating efficiencies below ~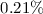 in
the nuclei, and between 0.25 and 0.36% at the outer positions.
Comparison with models of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) with
the standard ratios [
in
the nuclei, and between 0.25 and 0.36% at the outer positions.
Comparison with models of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) with
the standard ratios [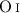 ](63)/[
](63)/[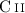 ]PDR and
([
]PDR and
([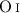 ](63)+[
](63)+[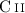 ]PDR) vs. TIR, the total infrared
intensity, yields two solutions. The physically most plausible
solution exhibits slightly lower densities and higher FUV fields
than found when using a full set of line ratios, [
]PDR) vs. TIR, the total infrared
intensity, yields two solutions. The physically most plausible
solution exhibits slightly lower densities and higher FUV fields
than found when using a full set of line ratios, [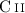 ]
]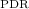 /[
/[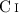 ](1–0), [
](1–0), [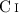 ](1–0)/CO(3–2), CO(3–2)/CO(1–0),
[
](1–0)/CO(3–2), CO(3–2)/CO(1–0),
[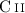 ]/CO(3–2), and, [
]/CO(3–2), and, [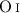 ](63)/[
](63)/[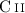 ]PDR. The best fits to
the latter ratios yield densities of 104 cm-3 and FUV
fields of ~
]PDR. The best fits to
the latter ratios yield densities of 104 cm-3 and FUV
fields of ~ –30 times the average interstellar field
without much variation. At the outer positions, the observed
total infrared intensities are in agreement with the derived best
fitting FUV intensities. The ratio of the two intensities lies at
4–5 at the nuclei, indicating the presence of other mechanisms
heating the dust. The [
–30 times the average interstellar field
without much variation. At the outer positions, the observed
total infrared intensities are in agreement with the derived best
fitting FUV intensities. The ratio of the two intensities lies at
4–5 at the nuclei, indicating the presence of other mechanisms
heating the dust. The [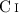 ] area filling factors lie below 2% at
all positions, consistent with low volume filling factors of the
emitting gas. The fit of the model to the line ratios improves
significantly if we assume that [
] area filling factors lie below 2% at
all positions, consistent with low volume filling factors of the
emitting gas. The fit of the model to the line ratios improves
significantly if we assume that [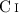 ] stems from a larger region
than CO 2–1. Improved modelling would need to address the filling factors of
the various submm and FIR tracers, taking into consideration the
presence of density gradients of the emitting gas by including
cloud mass and size distributions within the beam.
] stems from a larger region
than CO 2–1. Improved modelling would need to address the filling factors of
the various submm and FIR tracers, taking into consideration the
presence of density gradients of the emitting gas by including
cloud mass and size distributions within the beam.
Key words: galaxies: ISM / galaxies: structure / galaxies: individual: M 83, M 51 / ISM: structure / infrared: galaxies / submillimeter
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


