| Issue |
A&A
Volume 441, Number 2, October II 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 663 - 674 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20052995 | |
| Published online | 19 September 2005 | |
Orbital and spin variability of the intermediate polar BG CMi
1
University Observatory, Chungbuk National University, 361-763 Cheongju, Korea
2
Institute for Basic Science Research, Chungbuk National University, 361 763, Korea
3
Department of Astronomy, Odessa National University, T.G. Shevchenko Park, 65014 Odessa, Ukraine e-mail: il-a@mail.ru
4
Crimean Astrophysical Observatory, 98409 Nauchny, Ukraine
5
Korea Astronomy Observatory and Space Science Institute, Daejeon 305-348, Korea
Received:
4
March
2005
Accepted:
10
June
2005
Results of a CCD study of the variability of the
cataclysmic variable BG CMi obtained at the Korean 1.8 m telescope in
2002–2005 are presented. The “multi-comparison star” method had
been applied for better accuracy estimates. The linear ephemeris based on 19 mean maxima for 2002–2005 is HJD 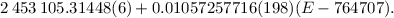 The period differs from that predicted by the quadratic ephemeris by Pych et al. (1996, AcA, 46, 279) leading to a possible cycle miscount. The statistically optimal ephemeris is a fourth-order polynomial, as a quadratic or even a cubic ephemeris leads to unaceptably large residuals: Min.HJD =
The period differs from that predicted by the quadratic ephemeris by Pych et al. (1996, AcA, 46, 279) leading to a possible cycle miscount. The statistically optimal ephemeris is a fourth-order polynomial, as a quadratic or even a cubic ephemeris leads to unaceptably large residuals: Min.HJD = 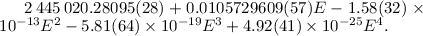 Thus the rate of the spin-up of the white dwarf is decreasing. An alternative explanation is that the spin-up has been stopped during recent years.
The deviations between the amplitudes of the spin variability in V and R, as well as between phases are not statistically significant. However, the orbital light curves exhibit distinct difference; the corresponding color index shows a nearly sinusoidal shape with a maximum at orbital phase ~0.2. The variations of the amplitude of spin waves shows a short maximum at the phase of the orbital dip. The corrected
ephemeris for orbital minima is
Min.HJD =
Thus the rate of the spin-up of the white dwarf is decreasing. An alternative explanation is that the spin-up has been stopped during recent years.
The deviations between the amplitudes of the spin variability in V and R, as well as between phases are not statistically significant. However, the orbital light curves exhibit distinct difference; the corresponding color index shows a nearly sinusoidal shape with a maximum at orbital phase ~0.2. The variations of the amplitude of spin waves shows a short maximum at the phase of the orbital dip. The corrected
ephemeris for orbital minima is
Min.HJD =  with a narrow dip occuring
0.07P later. The rate of the spin period variation seems to be
changed, justifying the necessity of regular observations of intermediate polars.
with a narrow dip occuring
0.07P later. The rate of the spin period variation seems to be
changed, justifying the necessity of regular observations of intermediate polars.
Key words: accretion, accretion disks / stars: individual: BG CMi / stars: individual: FO Aqr / stars: binaries: close / stars: novae, cataclysmic variables / stars: variables: general
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


