| Issue |
A&A
Volume 439, Number 3, September I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1057 - 1060 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042587 | |
| Published online | 12 August 2005 | |
Envelope models for the supersoft X-ray emission of V1974 Cyg
Institut d'Estudis Espacials de Catalunya and Institut de Ciències de l'Espai (CSIC), Campus UAB, Facultat de Ciències, Torre C5-parell, 2a planta, 08193 Bellaterra (Barcelona), Spain e-mail: [sala;hernanz]@ieec.uab.es
Received:
29
December
2004
Accepted:
7
February
2005
The evolution of the soft X-ray emission of V1974 Cyg
has been simulated by a white dwarf envelope model with steady hydrogen
burning. The comparison of the results obtained from ROSAT observations with
the results of our envelope models indicates that the post-outburst
evolution of the nova can be explained by steady H-burning
on either a 0.9 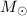 white dwarf with 50% degree
of mixing between solar-like accreted material and the
ONe degenerate core, or on a 1.0
white dwarf with 50% degree
of mixing between solar-like accreted material and the
ONe degenerate core, or on a 1.0 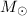 ONe white dwarf with 25% mixing.
ONe white dwarf with 25% mixing.
Key words: stars: individual: V1974 Cygni / stars: novae, cataclysmic variables / stars: white dwarfs / X-rays: binaries
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


