| Issue |
A&A
Volume 438, Number 2, August I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 545 - 556 | |
| Section | Galactic structure, stellar clusters, and populations | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042035 | |
| Published online | 08 July 2005 | |
Modelling the Milky Way through adiabatic compression of cold dark matter haloes
1
Dipartimento di Fisica “E.R. Caianiello”, Università di Salerno, and INFN, Sez. di Napoli, Gruppo Coll. di Salerno, via S. Allende, 84081 Baronissi (Salerno), Italy e-mail: winny@na.infn.it
2
Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli, and INFN, Sez. di Napoli, Complesso Universitario di Monte S. Angelo, via Cinthia, 80126 Napoli, Italy
3
Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica – Osservatorio Astronomico di Capodimonte, Salita Moiariello 16, 80131 Napoli, Italy
Received:
21
September
2004
Accepted:
19
January
2005
We use the adiabatic compression theory to build a physically well-motivated Milky Way mass model in agreement with observational data. The visible mass of the Galaxy is distributed in a spheroidal bulge and a multi-component disc parametrized by three galactic parameters, the Sun distance to the galactic centre, R0, the total bulge mass,  , and the local disc surface density,
, and the local disc surface density, 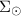 . To model the dark matter component, we adiabatically compress a Navarro, Frenk and White (NFW) halo (with concentration c and total mass
. To model the dark matter component, we adiabatically compress a Navarro, Frenk and White (NFW) halo (with concentration c and total mass  ) for fixed values of the spin parameter λ, the fraction of the mass in baryons mb, and the thin disc contribution to total angular momentum jd. An iterative selection procedure is used to explore in detail the wide space of parameters only selecting those combinations of
) for fixed values of the spin parameter λ, the fraction of the mass in baryons mb, and the thin disc contribution to total angular momentum jd. An iterative selection procedure is used to explore in detail the wide space of parameters only selecting those combinations of  that give rise to a Milky Way model in agreement with observational constraints. This analysis leads us to conclude that only models with
that give rise to a Milky Way model in agreement with observational constraints. This analysis leads us to conclude that only models with 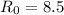 kpc,
kpc,  and
and 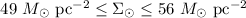 can be reconciled with the set of observational constraints. As regards the parameters entering the adiabatic compression, we find
can be reconciled with the set of observational constraints. As regards the parameters entering the adiabatic compression, we find 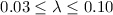 and
and 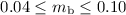 , while final estimates of the parameters describing the initial halo profile turn out to be
, while final estimates of the parameters describing the initial halo profile turn out to be 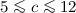 and
and 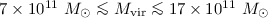 (all at 95.7% CL).
(all at 95.7% CL).
Key words: Galaxy: kinematics and dynamics / Galaxy: structure / galaxies: formation / dark matter
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


