| Issue |
A&A
Volume 438, Number 1, July IV 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 127 - 137 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20052703 | |
| Published online | 06 July 2005 | |
Dark matter in the inner parts of barred galaxies: The data
1
Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of Groningen, Postbus 800, Groningen 9700 AV, The Netherlands e-mail: isa@astro.rug.nl
2
RSAA, Mount Stromlo Observatory, Cotter road, Weston Creek, ACT 2611, Australia
3
Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía (CSIC), Apartado 3004, 18080 Granada, Spain
4
Geneva Observatory, Ch. des Maillettes 51, 1290 Sauverny, Switzerland
Received:
14
January
2005
Accepted:
11
April
2005
This paper presents surface photometry 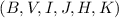 and Hα rotation curves of 27 isolated spiral galaxies. The
final goal is to obtain the mass distribution of a sample of isolated
spiral galaxies in order to model their gas kinematics. This is then
compared to the observed rotation curve, to determine the necessity of
a dark halo in the inner parts (Perez et al. 2004, A&A, 424, 799). The azimuthally averaged
radial surface brightness profiles and the integrated magnitudes
obtained from ellipse fitting are given for each of the sample
galaxies. The ellipse fitting technique applied to the light
distribution also allowed us to obtain the size of the bar, and the
inclination and position angle of the outer isophotes that allow the
galaxy deprojection. Using these profiles, 1-D disk-bulge
decomposition was performed to obtain the disk scale-length and the
bulge effective radius for the different bands. Through the fitting
of a parametric function to the observed rotation curve, the maximum
rotational velocity and the corresponding radius was obtained. The
correlation between the bulge and disk parameters is in agreement with
previous studies (de Jong 1996a, A&A, 313, 45; Márquez & Moles 1999,
A&A, 344, 421; Baggett et al. 1998, AJ, 116, 1626).
Regarding the
Kormendy relation (Kormendy 1977,
ApJ, 218, 333), in agreement with de Jong, no
correlation between the bulge effective radius and its surface
brightness is found, possibly due to the small range of bulge
magnitudes covered. We find a smaller scatter in the structural
relations when compared to non-isolated samples in agreement with
Márquez & Moles (1999). Finally, a correlation between the disk scale-length
and the bar size is observed, possibly reflecting the rapid growth of
a bar.
and Hα rotation curves of 27 isolated spiral galaxies. The
final goal is to obtain the mass distribution of a sample of isolated
spiral galaxies in order to model their gas kinematics. This is then
compared to the observed rotation curve, to determine the necessity of
a dark halo in the inner parts (Perez et al. 2004, A&A, 424, 799). The azimuthally averaged
radial surface brightness profiles and the integrated magnitudes
obtained from ellipse fitting are given for each of the sample
galaxies. The ellipse fitting technique applied to the light
distribution also allowed us to obtain the size of the bar, and the
inclination and position angle of the outer isophotes that allow the
galaxy deprojection. Using these profiles, 1-D disk-bulge
decomposition was performed to obtain the disk scale-length and the
bulge effective radius for the different bands. Through the fitting
of a parametric function to the observed rotation curve, the maximum
rotational velocity and the corresponding radius was obtained. The
correlation between the bulge and disk parameters is in agreement with
previous studies (de Jong 1996a, A&A, 313, 45; Márquez & Moles 1999,
A&A, 344, 421; Baggett et al. 1998, AJ, 116, 1626).
Regarding the
Kormendy relation (Kormendy 1977,
ApJ, 218, 333), in agreement with de Jong, no
correlation between the bulge effective radius and its surface
brightness is found, possibly due to the small range of bulge
magnitudes covered. We find a smaller scatter in the structural
relations when compared to non-isolated samples in agreement with
Márquez & Moles (1999). Finally, a correlation between the disk scale-length
and the bar size is observed, possibly reflecting the rapid growth of
a bar.
Key words: galaxies: fundamental parameters / galaxies: structure / galaxies: photometry / galaxies: kinematics and dynamics
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


