| Issue |
A&A
Volume 435, Number 1, May III 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 43 - 64 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042271 | |
| Published online | 25 April 2005 | |
A dichotomy in the orientation of dust and radio jets in nearby low-power radio galaxies
1
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Strasse 2, 85748, Garching bei München, Germany e-mail: gverdoes@eso.org
2
Sterrewacht Leiden, Postbus 9513, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands e-mail: dezeeuw@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Received:
28
October
2004
Accepted:
28
January
2005
We examine the properties of central dust in nearby quiescent and
active early-type galaxies. The active galaxies are low-power radio galaxies
with Fanaroff & Riley type I or I/II radio jets. We focus on (a) the comparison
of the dust distributions in the active and quiescent galaxy samples;
and (b) the relation between the radio jet and dust orientations. Our
main observational conclusions are: (i) in line with previous
studies, the dust detection rate is higher in radio-jet galaxies than
in non radio-jet galaxies; (ii) radio galaxies contain a higher
fraction of regular dust “ellipses” compared to quiescent galaxies
which contain more often irregular dust distributions; (iii) the
morphology, size and orientation of dust ellipses and lanes in
quiescent early-types and active early-types with kpc-scale radio jets
is very similar; (iv) dust ellipses are aligned with the major axis of
the galaxy, dust lanes do not show a preferred alignment except for
large (>kpc) dust lanes which are aligned with the minor axis of the
galaxy; and (v) as projected on the sky, jets do not show a preferred
orientation relative to the galaxy major axis (and hence dust
ellipses), but jets are preferentially perpendicular to dust lanes.
We show that the dust ellipses are consistent with being nearly
circular thin disks viewed at random viewing angles. The
lanes are likely warped dust structures, which may be in the
process of settling down to become regular disks or are being perturbed by a non-gravitational force. We use the observed dust-jet orientations to constrain the
three-dimensional angle 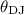 between jet and dust.
For dust-lane galaxies, the jet is approximately perpendicular to the
dust structure, while for dust-ellipse galaxies there is a much wider
distribution of
between jet and dust.
For dust-lane galaxies, the jet is approximately perpendicular to the
dust structure, while for dust-ellipse galaxies there is a much wider
distribution of 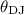 .
We discuss two scenarios that could explain the dust/jet/galaxy orientation dichotomy.
If lanes are indeed settling, then the jet orientation apparently is roughly
aligned with the angular momentum of the dust before it settles.
If lanes are perturbed by a jet-related force, it appears that it causes the dust to move out of its equilibrium plane in the galaxy into a plane which is perpendicular to the jet.
.
We discuss two scenarios that could explain the dust/jet/galaxy orientation dichotomy.
If lanes are indeed settling, then the jet orientation apparently is roughly
aligned with the angular momentum of the dust before it settles.
If lanes are perturbed by a jet-related force, it appears that it causes the dust to move out of its equilibrium plane in the galaxy into a plane which is perpendicular to the jet.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: elliptical and lenticular, cD / galaxies: nuclei / galaxies: jets / ISM: dust, extinction
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


